FIG 8 .
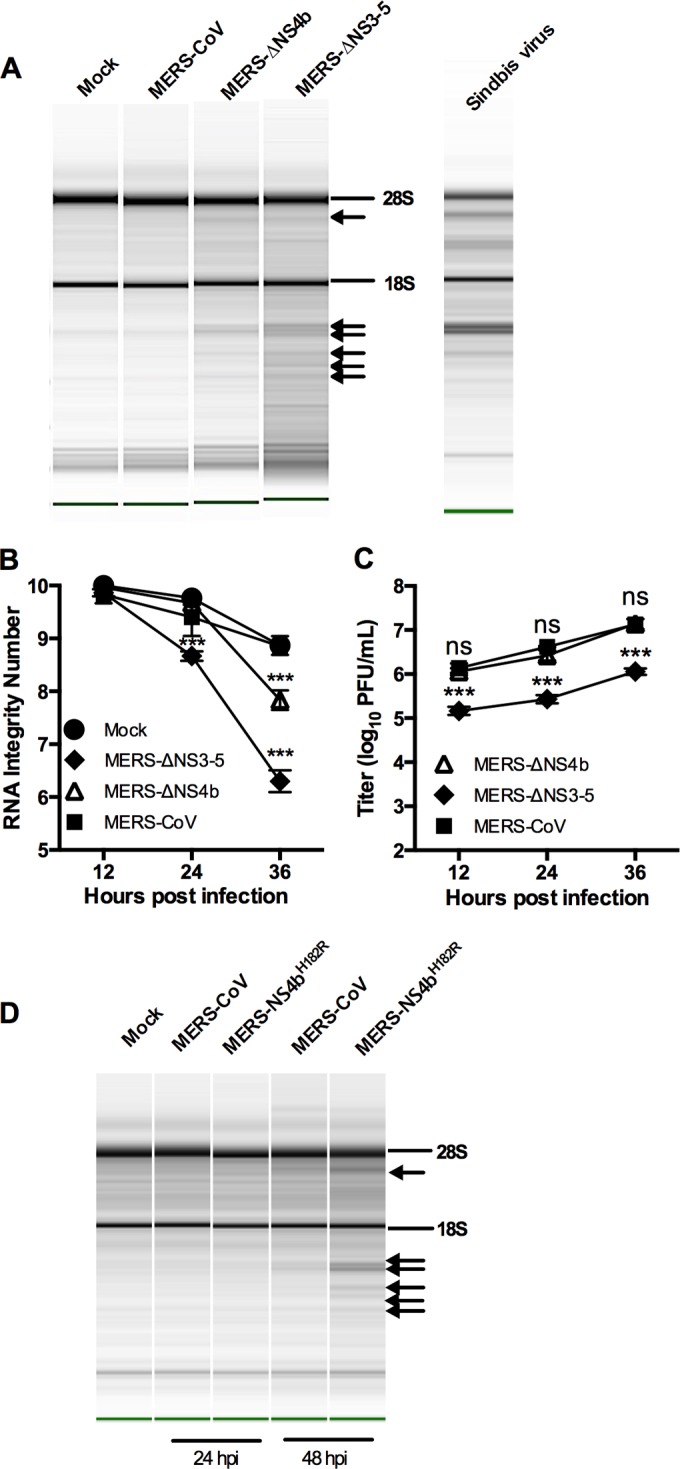
MERS-CoV inhibits rRNA degradation in human airway cells. (A to C) rRNA degradation pattern from cells 36 h postinfection (A), quantification by RNA integrity number (RIN) (B), and replication kinetics (C) of mock-infected and MERS-CoV-, MERS-ΔNS4b-, and MERS-ΔNS3-5-infected Calu-3 cells (MOI of 1 PFU; n = 3). Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons and indicated as follows: ***, P value of <0.001; ns, not significant. Values are means ± SEM (error bars). RNA from Sindbis virus-infected human A549 cells (run separately on the Agilent Bioanalyzer) is shown in panel A as a marker for the RNase L-induced pattern of degradation of human rRNA. (D) rRNA degradation pattern from cells 24 and 48 h after MERS-NS4bH182R infection of Calu-3 cells. The positions of 28S and 18S rRNAs are indicated in panels A and D. Data shown are from one representative experiment of two.
