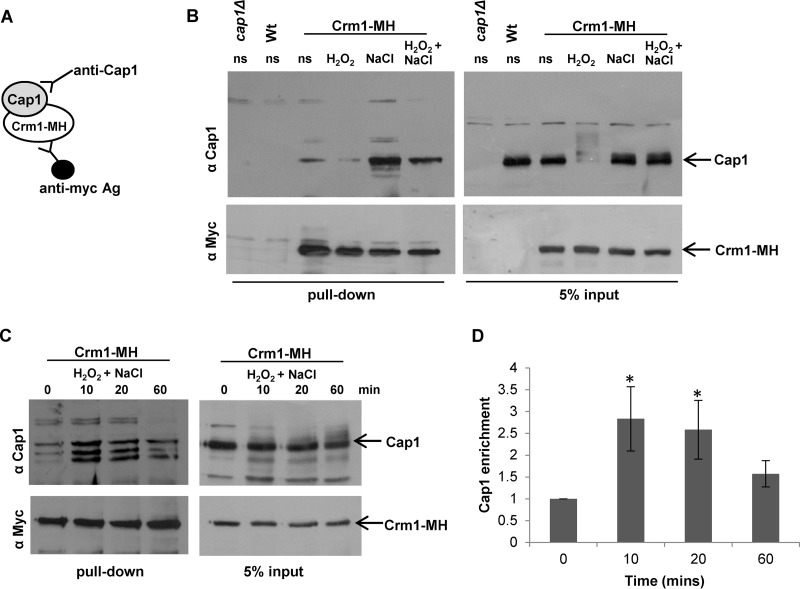
FIG 7 .
Cationic stress promotes Cap1 interaction with the Crm1 nuclear export factor. (A) Strategy used to examine Cap1 association with Crm1. (B) Stress effects on Cap1 interaction with Crm1. Extracts were prepared from wild-type cells (Wt [JC747]), cap1Δ cells (JC842), and wild-type cells expressing 2Myc- and 6His-tagged Crm1 (Crm1-MH [JC1925]) before (ns) and following exposure to 5 mM H2O2, 1 M NaCl, or combinations of the stresses for 10 min. Crm1-MH was immunoprecipitated using anti-Myc agarose, and precipitated proteins and 5% input were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Coprecipitation of Cap1 was assayed by Western blotting using an anti-Cap1 antibody (top panel), and precipitation of Crm1-MH was assayed using anti-Myc antibodies (bottom panel). (C) The increased interaction of Cap1 with Crm1 following combinatorial stress is transient. Cap1 interaction with Crm1 was analyzed as described for panel B before (ns) and following treatment of Crm1-MH cells with 5 mM H2O2 plus 1 M NaCl for the times indicated. (D) Quantification of the increased interaction of Cap1 with Crm1 following combinatorial stress. Quantitative densitometric analysis of Western blots from four biological replicates was conducted to determine the fold enrichment of Cap1 interaction with Crm1 relative to time zero. Mean values (±standard errors of the mean [SEM]) are shown, and ANOVA was used to determine statistically significant differences in Cap1 enrichment levels (*, P < 0.01).