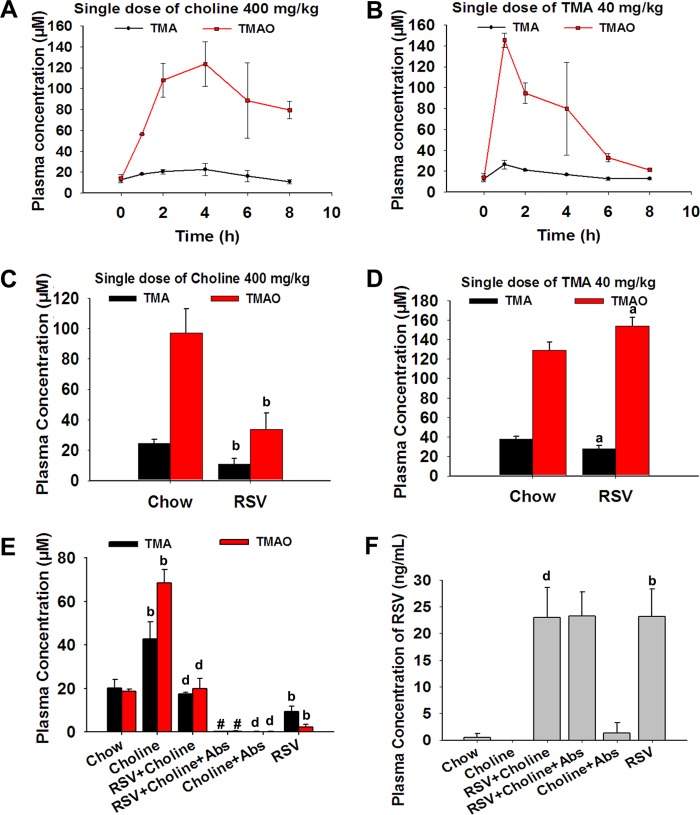
FIG 1 .
RSV inhibited TMAO synthesis in C57BL/6J mice. (A and B) Eight-week-old female C57BL/6J mice were administered choline (400 mg/kg of body weight, n = 10) (A) or TMA (40 mg/kg, n = 10) (B). Blood samples were collected at the indicated times. Serum TMA and TMAO levels were determined by LC/MS. (C and D) Eight-week-old female C57BL/6J mice were fed a chow diet with or without RSV (0.4%) in the presence or absence of choline (1%) or Abs. After 30 days, several mice of the chow-and-RSV-fed group were administered choline (400 mg/kg, n = 10) (C) or TMA (40 mg/kg, n = 10) (D). At 4 h after choline was given, or 1 h after TMA was given, the mice were euthanized and blood was collected. Serum TMA and TMAO levels were determined by LC/MS. (E and F) The other mice were also euthanized, and blood was collected. Serum TMA and TMAO levels (E) and RSV levels (F) were determined by LC/MS. Values are presented as means ± SD (n = 10). a, P < 0.05; b, P < 0.01 (versus vehicle-treated control group); d, P < 0.01 (versus choline-treated group); #, P < 0.05 (versus group cotreated with choline and RSV).