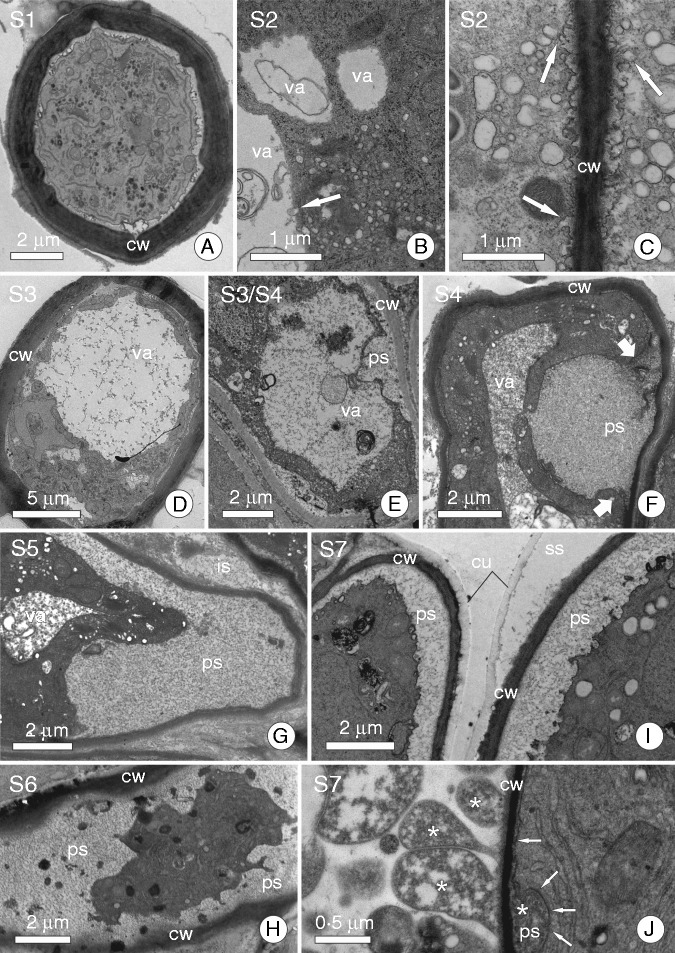
Fig. 2.
Ultrastructure of some secretory cells showing different secretory structures in order to demonstrate the stages of the secretory cycle. (A) Aechmea blanchetiana (Bromeliaceae) mucilage-secreting trichome; cell in stage S1. (B) Secretory cell from stem epidermis of Schizolobium parahyba (Fabaceae) showing vesicles from dictyosomes merging with the large vacuole; a characteristic of stage S2. (C) Secretory cell of a floral nectary from Erythrina speciosa (Fabaceae); arrows indicate fusion of small vesicles to the plasma membrane to discharge secretion in stage S2. (D) Aechmea blanchetiana (Bromeliaceae) mucilage-secreting trichome with a large central vacuole full of mucilage (stage S3). (E) Cell from a colleter of Calycophyllum spruceanum (Rubiaceae) in a stage similar to that shown in D (S3), but here we note that the plasma and vacuolar membranes are closer to the periplasmic space. (F) Secretory cell of a colleter from Caryocar brasiliense (Caryocaraceae); arrows indicate edges of a vacuole that has just merged with the plasma membrane and secretion from within the vacuole in the periplasmic space; a characteristic of stage S4. (G, H) Secretory cell of a colleter from C. brasiliense (Caryocaraceae) and Tontelea micrantha (Celastraceae), respectively. Note the secretion is in the periplasmic space and the protoplast has become dark and compressed (stages S5 and S6). (I) Nectar-secreting cell from floral nectary of Luehea grandiflora (Malvaceae) in stage S7; note that the protoplast presses secretion against the cell wall, causing it to cross the cell wall and accumulate in the subcuticular space. (J) Secretory cell of a colleter from Plumeria rubra (Apocynaceae). Arrows indicate the plasma membrane and a rubber-like secretion in the periplasmic space; this secretion is being pressed against the cell wall, causing it to cross into the intercellular space (stage S7). Abbreviations: cw, cell wall; cu, cuticle; ps, periplasmic space; ss, subcuticular space; va, vacuole.