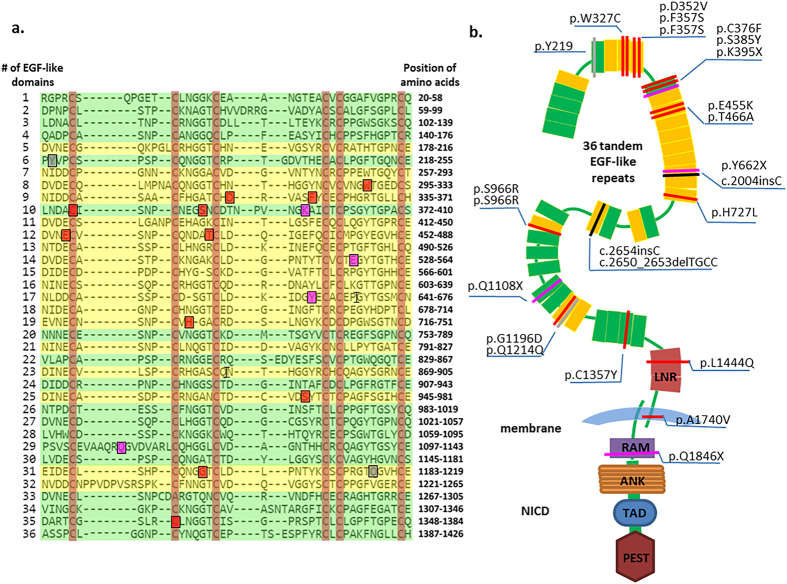
Figure 2. Somatic mutations distributed across the region of NOTCH1 receptor in 23 HNSCC patients.
(a) An alignment of 36 tandem EGF-like domains of human NOTCH1 extracted from the UniProt protein database and generated by Align tools using the Clustal Omega programme according to the EGF-like repeats consensus. Each line represents a conserved EGF-like domain, consensus site for Ca2+ dependent binding (shaded yellow) and non-Ca2+ binding (shaded green) among 36 EGF-like repeats in the extracellular domains of a fold “triple-stranded” structure model. Red highlighting indicates six conserved Cysteine residues of the EGF-like domain to form consensus disulfide bonds. Blue and green boxes show the somatic mutation identified from this study of 124 HNSCC patients. Grey, red and purple shading in boxes show synonymous, missense and nonsense somatic mutations at the EGF-like domain, respectively. The symbol of “I” indicates the frameshift mutation. (b) Schematic diagram of the domain organization of the human NOTCH1 gene generated by the SMART database including 36 tandem EGF-like repeats (colour yellow and green indicate the Ca2+-dependent and non- Ca2+ binding domain, respectively; rectangle) and 3 Lin-12/Notch repeats (LNR; colour green; rectangle), 2 hetero- dimerization domain (HD; Colour grey; rectangle) determined as negative regulatory regions. A short transmembrane segment (TM; colour blue; arc). The Notch intracellular domain (NICD) contains the recombination signal-binding protein 1 for J (RBP-J) association molecule (RAM; colour red; rectangle), Ankyrin repeats (ANK; colour orange; rectangle), transcriptional activation domain (TAD; colour deep blue; rectangle) and proline, glutamic acid, serine/threonine-rich motif (PEST; colour brown; rectangle). Each colour bar represents a NOTCH1 somatic mutation in an HNSCC individual, of the class of mutation type indicated the same colour as (a).