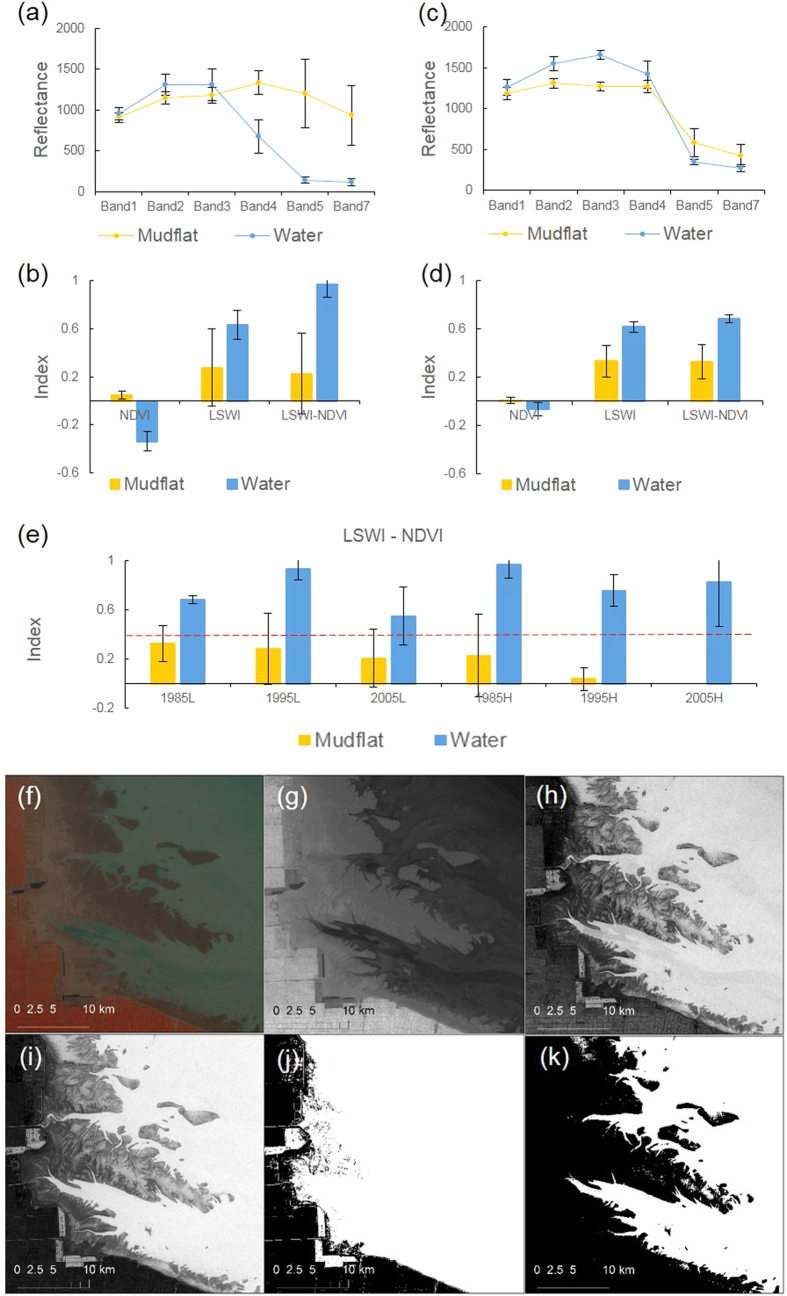
Figure 4. Information used to develop an algorithm to determine shorelines in the Yangtze Estuary.
Processed by ArcGIS 10.1 and ENVI 5.2 (a) The reflectance difference of barren mudflat and seawater during low tide. Landsat image LT51180381985052HAJ00 is used as an example. (b) The differences of NDVI, LSWI, and “LSWI - NDVI” between barren mudflat and seawater during low tide. (c) The reflectance difference of barren mudflat and seawater during high tide. Landsat image LT51180381985324HAJ00 is used as an example. (d) The NDVI, LSWI, and “LSWI − NDVI” differences of barren mudflat and seawater during high tide. (e) The use of a fixed threshold of 0.5 for “LSWI − NDVI” images for distinguishing barren mudflat from seawater. 1985L: the lowest tide shoreline in 1985, 1995L: the lowest tide shoreline in 1995, 2005L: the lowest tide shoreline in 2005, 1985H: the highest tide shoreline in 1985, 1995H: the highest tide shoreline in 1995, 2005H: the highest tide shoreline in 2005. (f) False color composite Landsat image (musR/G/B = NIR/Red/Green) of LT51180381985052HAJ00. Source: the U.S. Geological Survey. Available at: http://www.usgs.gov. (g) NDVI. (h) LSWI. (i) LSWI − NDVI. (j) LSWI > NDVI. White indicates water, Black indicates non-water. (k) LSWI > NDVI + 0.5.