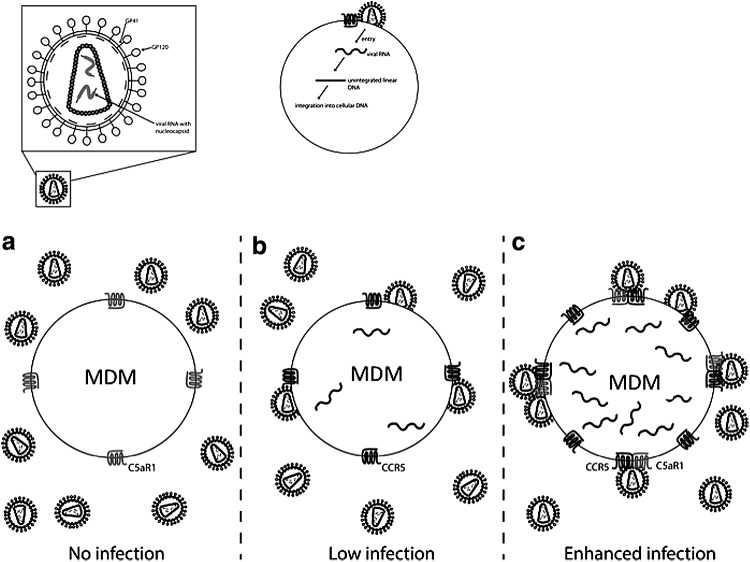
FIG. 6.
Model depicting the impact of C5aR1 CCR5 association on HIV infection. (a) When MDM express C5aR1 but lack CCR5, as in homozygous CCR5Δ32 individuals, R5-tropic HIV strain YK-JRCSF does not enter the target cell. (b) MDM become infected by R5-tropic HIV strains when they express CCR5. (c) When C5aR1 and CCR5 are both expressed in MDM, they tend to form heterodimers. Our data indicate that such heterodimer formation is associated with enhanced infection of R5-tropic strains, as the virus seems to preferentially infect cells that express both receptors at high levels.