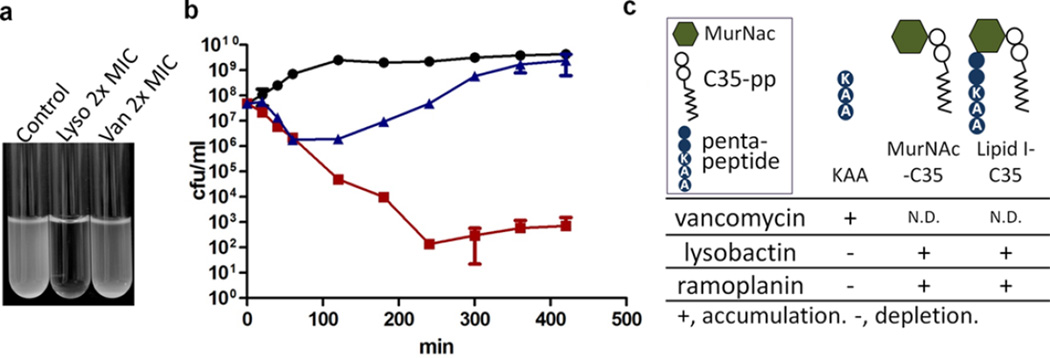
Figure 3.
Lysobactin causes rapid lysis of S. aureus. (a) Cultures treated with lysobactin or vancomycin at 2× MIC. (b) Kill curves for S. aureus treated with no antibiotic (black circles), vancomycin (blue triangles), or lysobactin (red squares) at 2× MIC. (c) Addition of exogenous sugar–pyrophophate–lipids (5 µM) rescued S. aureus from killing by lysobactin (see Figure S3).