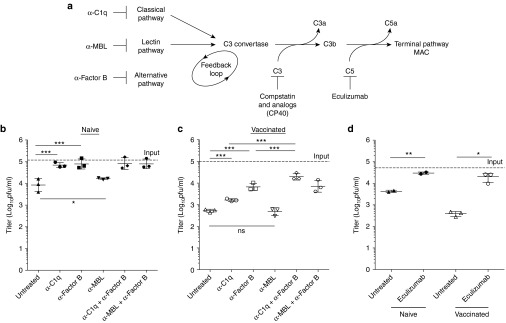
Figure 2.
Mechanistic characterization of complement and antibody mediated neutralization of vaccinia virus. (a) Complement pathway schematic and targets of inhibitory antibodies. Complement activation pathway dissection in naive (b) or immune (c) plasma. Selective inhibition of the various pathways of the complement cascade demonstrates their contribution to viral neutralization. Plasma from naive and immune donors was pretreated with 500 μg/ml 1379 (anti-Factor B) or 100 μg/ml P1H10 (anti-C1q) or 60 μg/ml F38 (anti-MBL) or 50 μg/ml of eculizumab (anti-C5) (d) to allow for binding. Vaccinia virus neutralization over the course of a 1 hour incubation period at 37 °C (2 × 105 pfu/ml) was subsequently assessed by plaque assay (n = 3 donors per immune status with the exception of naive eculizumab samples n = 2). Data are represented as group means ± SD. Each dot represents a donor. (***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ns = p > 0.05).