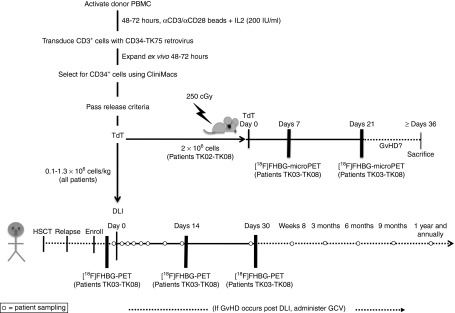
Figure 1.
Detailed study schema. Activated donor T cells were retrovirally transduced to express CD34-TK75. After in vivo expansion and selection for CD34, TdT, cells were required to meet the following release criteria: ≥50% viable, ≥ 10% transduced, ≥85% CD34+, ≥80% sensitive to ganciclovir (GCV) in vitro, ≥1 × 105 TdT/kg patient weight, no detectable endotoxin or Mycoplasma, no growth in 14 days aerobic or anaerobic microbial culture medium. Patients received a donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) of purified retrovirally transduced donor T cells on day 0. Blood samples were collected for patient safety assessments and correlative studies (open circles) at approximately 30 minutes, 2 hours, 24 hours; days 2, 5, and 7; weeks 2, 4, and 8; months 3, 6, 9, and 12; and then annually for as long as patients remained enrolled in the trial. Patients TK03 to TK08 were additionally enrolled in a subprotocol in which they were imaged at baseline and on days +14 and +30 using [18F]FHBG PET/CT to detect the TdT. If graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) developed post-DLI, GCV (5 mg/kg) was administered twice daily for 7 days to investigate the use of suicide-gene mediated treatment via selective killing of the transduced donor T cells. Collection of blood samples was then reinitiated on the same schedule as outlined above, but using the day of GCV administration as day 0. A portion of the TdT (≤2 × 106 cells) prepared for patients TK02-TK08 was infused in parallel into NSG mice (Figure 8) that were followed for symptoms of GvHD and imaged via [18F]FHBG microPET/CT on days 7 and 21 postinfusion. HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.