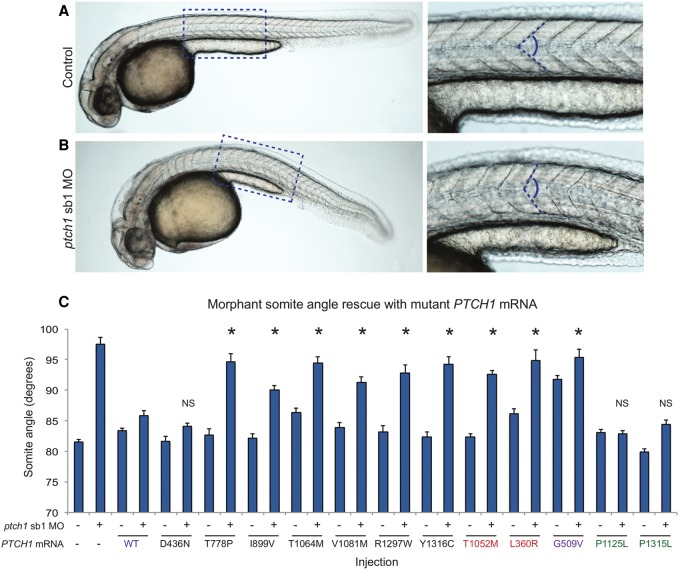
Figure 2.
PTCH1 variants identified in ODA patients are pathogenic. (A,B) Representative lateral images of uninjected control and ptch1 sb1 MO-injected live embryos taken at 36 h post-fertilization (hpf); dashed boxes are enlarged in the insets (right). Magnified panels show chevron-shaped somites (controls) and abnormal-shaped somites (morphants), caused by aberrant Hedgehog signaling in the zebrafish myotome. Dashed blue lines indicate measurement position (at the midpoint between the proximal hindgut and the anus) used for phenotypic scoring of embryo batches. (C) All six nonsynonymous PTCH1 variants identified in ODA cases were pathogenic as indicated by the inability of mutant mRNA to rescue the ptch1 MO-induced somite angle defects. PTCH1 p.Thr1052Met, a rare variant (minor allele frequency in controls 0.001; n = 13,006 chromosomes [EVS]) reported previously in HPE, is also pathogenic; p.Leu360Arg is a previously reported functional null. Rescue with a common PTCH1 p.Pro1315Leu encoding variant (rs357564; present in homozygosity in 8% of controls; n = 12,568 chromosomes in EVS) was not significantly (NS) different from wild type (WT), nor was a previously reported benign variant p.Pro1125Leu change, providing support for the specificity of the assay. p.Gly509Val is a positive control for dominant negative effects. The missense variant p.Asp436Asn identified in the ODA control C2 was benign in this assay. We measured 38–58 embryos per injection batch with blind scoring. Asterisks indicate statistical differences between mutant and WT rescue (P < 0.0001; Student's t-test). Error bars, SEM. See Supplemental Table 7 for somite measurement data.