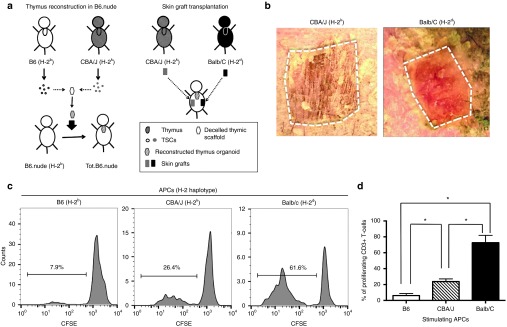
Figure 6.
Induction of donor-specific immune tolerance with thymus organoids reconstructed of both donor and recipient thymic epithelial cells (TECs). (a) The schematic drawing shows the strategy of the experiment. TECs were isolated from B6 and CBA/J mice and mixed at 1 : 1 ratio. The thymus organoids were reconstructed with B6 Lin-bone marrow progenitors and TECs at 1 : 1 ratio (2 × 105 each), and transplanted underneath the kidney capsules of B6.nude mice. Ten weeks postoperatively, skin grafts harvested from CBA/J and Balb/C (third-party allografts) mice were transplanted to the Tot.B6.nude mice (n = 4). Graft survival was monitored for up to 4 weeks. (b) Representative photographic images of skin grafts (outlined) on Tot.B6.nude at 22 days postoperatively. While the third-party allograft (left panel, Balb/C) is largely rejected, the CBA/J allograft (right panel) is well tolerated. (c,d) Mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) experiments, showing the proliferation responses of CD3+ T-cells of the recipient Tot.B6.nude mice (n = 4) in the presence of syngeneic or allogeneic APCs. (c) Representative carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE) dilution histogram: Left panel, syngeneic B6 APCs; middle panel, CBA/J allogeneic APCs; right panel, third-party allogeneic APCs. (d) Percentages of proliferating CD3+ T-cells. *P < 0.05, nonparametric Mann–Whitney test.