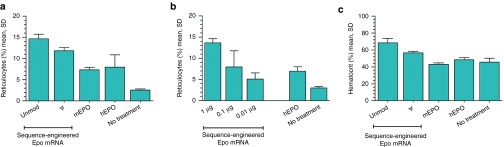
Figure 3.
Sequence engineered Epo mRNA elicits physiological effects in mice. (a) Sequence-engineered mouse Epo mRNA elicits strong reticulocyte responses in mice. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with either TransIT-complexed mRNA (1 μg) or recombinant erythropoietin (EPO) protein (hEPO: 100 U, mEPO: 800 ng). mRNA was either unmodified or harbored pseudouridine. The level of reticulocytes was determined 4 days after treatment. (b) Low nanogram doses of engineered but unmodified mouse Epo mRNA elicit substantial reticulocyte responses in mice. The indicated doses of TransIT-complexed Epo mRNA or 100 U of hEPO were intraperitoneally administered to mice. Reticulocytes were quantified 4 days after injection. (c) Sequence-engineered mouse Epo mRNA substantially increases the hematocrit in mice. Mice were treated with either TransIT-complexed mRNA (1 μg) or recombinant EPO protein (hEPO: 100 U, mEPO: 800 ng) on day 0 and 14. The hematocrit was measured on day 18. mRNA was either unmodified or harbored pseudouridine. unmod, engineered mRNA harboring the nucleotides A, U, G, and C; ψ, engineered mRNA in which pseudouridine replaces U; hEPO, recombinant human Epo protein; mEPO, recombinant murine Epo protein. n = 4 for all groups.