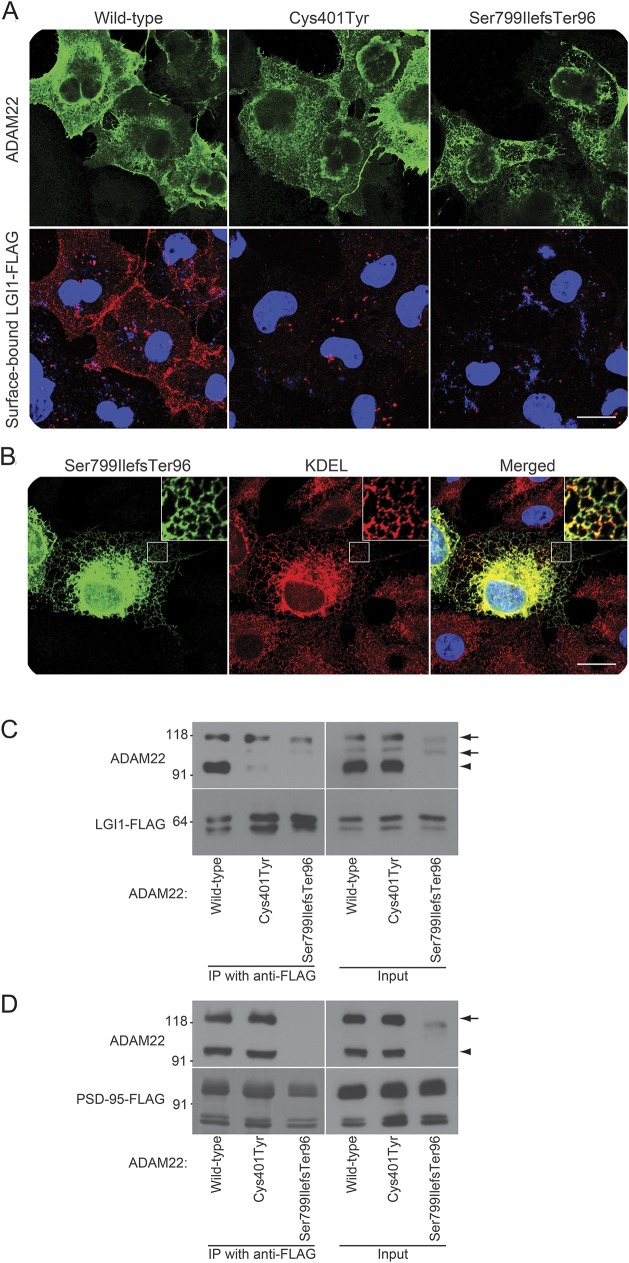
Figure 3. ADAM22 mutant proteins do not bind to LGI1.
(A) Fluorescent confocal microscope images from the cell surface binding assay, in which indicated ADAM22 complementary DNAs were cotransfected with wild-type FLAG-tagged LGI1 into COS7 cells. Surface-bound FLAG-tagged LGI1 was labeled before cell permeabilization (red) and then ADAM22 was stained (green). Both ADAM22 mutants fail to bind to LGI1. Bar: 20 μm. (B) Ser799IlefsTer96 mutant (green) is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum labeled by the anti-KDEL antibody (red). Regions outlined with white squares are magnified in the upper right of the images. Bar: 20 μm. (C, D) Immunoprecipitation of ADAM22 mutants with FLAG-tagged LGI1 (C) or PSD-95 (D) in HEK293T cells. Neither ADAM22 mutant binds to LGI1 (left panel in C). The Cys401Tyr mutant binds to PSD-95, but the Ser799IlefsTer96 mutant does not (left panel in D). Arrows and arrowheads indicate the positions of immature and mature ADAM22, respectively. Immature ADAM22 is often observed in overexpressed cells and seems to nonspecifically bind to LGI1 under these conditions, whereas in the brain the immature band is not observed.