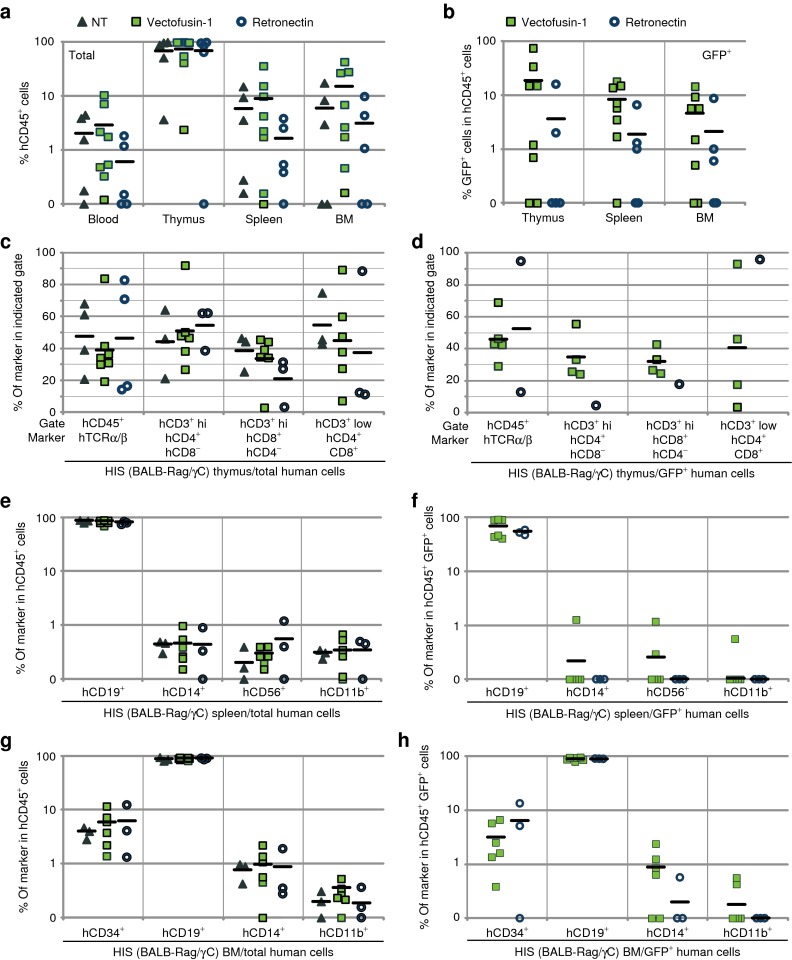
Figure 5.
Evaluation of the safety of Vectofusin-1 in the immunodeficient BALB-Rag/γC mouse model. hCD34+ cells were transduced for 6 hours with GALVTR-LVs either in the presence of 12 µg/ml of Vectofusin-1 (squares) or 20 µg/cm2 of Retronectin (circle) and injected into the liver of newborn mice. Controls (NT) included non-infected cells not exposed to any transduction enhancer (triangle). (a,b) Eleven to thirteen weeks post-injection, the engraftment of human transduced cells into HIS (BALB-Rag/γC) mice was measured by flow cytometry in the peripheral blood, the thymus, the spleen, and the bone marrow (BM) using anti-hCD45 antibodies and green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression levels. (c,d) Human T lymphopoiesis was measured in the thymus by monitoring human TCRα/β in the hCD45+ gate, and CD4 and CD8 marker expression in CD3+ low or high (hi) gates. Human B lymphoid development, monocytes, natural killer cells, granulocytes, and hematopoietic progenitors were determined in the (e,f) spleen or the (g,h) BM by monitoring, respectively, the human CD19, CD14, CD56, CD11b, and CD34 surface markers in the hCD45+ gate. GALV, gibbon ape leukemia virus; HIS, human immune system; LV, lentiviral vector; NT, not transduced; TCRα/β, T-cell receptor α/β.