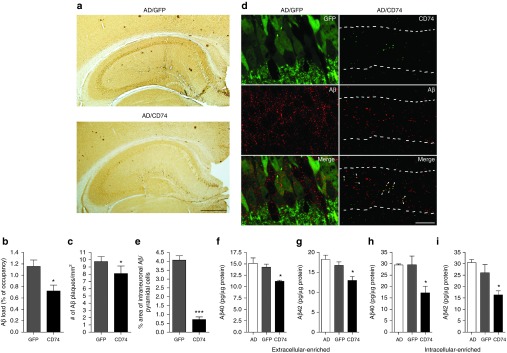
Figure 4.
CD74 attenuates Aβ loads in the hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease (AD) mice. (a) Representative images of Aβ staining in the hippocampus of AAV-TRE-GFP or AAV-TRE-CD74-injected AD mice. Scale bar = 500 µm. (b,c) Quantification of total Aβ loads (b) and number of Aβ plaques (c) in the hippocampal region (n = 6 per group, 10 sections per brain). (d) Confocal microscopy shows intraneuronal accumulation of Aβ (red) in GFP or CD74-positive neurons (green). Numbers of Aβ are observed in GFP-positive neurons but not in CD74-positive neurons. CD74 expression is colocalized with Aβ (arrowheads). Pyramidal cell layer is indicated with broken lines. 630× magnification. Scale bar = 10 μm. (e) Quantification of intraneuronal Aβ in pyramidal neurons (n = 10). (f–i) The levels of Aβ40 (f,h) and Aβ42 (g,i) in extracellular (f,g) and intracellular (h,i)-enriched fractions were measured by human Aβ40- and Aβ42-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (n = 8). Bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean. * denotes P < 0.05 as determined by Student's t-test. AAV, adeno-associated virus; GFP, green fluorescent protein; TRE, tet-response element.