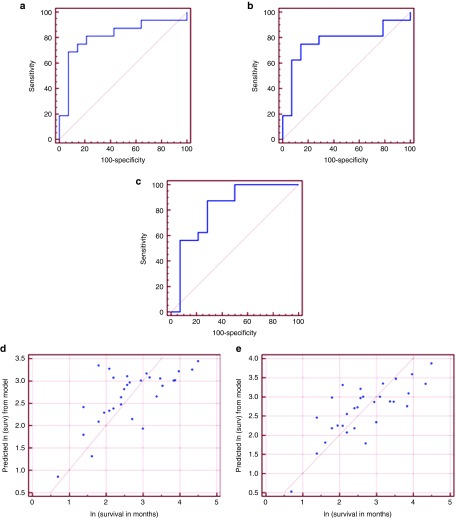
Figure 1.
miRNA-based statistical models can predict renal cell carcinoma patients' survival under sunitinib treatment. (a–c) Multivariate logistic regression models to predict renal cell carcinoma patients' survival under sunitinib treatment as a dichotomous variable. Patients were divided into short-term (<12 months) versus long-term (≥ 12 months) survival under sunitinib. (a) Model 1: based on the expression of miR-1225-3p and miR-208 (AUC = 0.812, 95% CI: (0.629, 0.931), P = 0.0003). At a cut-off probability of 0.70, positive predictive value (PPV) = 92% and at a cutoff probability of 0.28, negative predictive value (NPV) = 80%. (b) Model 2: based on the expression ofmiR-1225-3P and miR-155-3p (AUC = 0.772, 95% CI: (0.583, 0.905), P = 0.0042). At a cut-off probability of 0.70, PPV = 91% and at a cut-off probability of 0.40, NPV = 77%. (c) Model 3: based on the expression of miR-597 and miR-1 (AUC = 0.812, 95% CI: (0.629, 0.931), P = 0.0003). At a cut-off probability of 0.80, PPV = 90% and at a cut-off probability of 0.21, NPV = 100%. (d,e) Multivariate regression models predict patients' survival under sunitinib treatment as a continuous variable. (d) miR-874 and miR-221 model (P = 0.0003). (e) miR-874, miR-221, and miR-424 model (P = 0.0001).