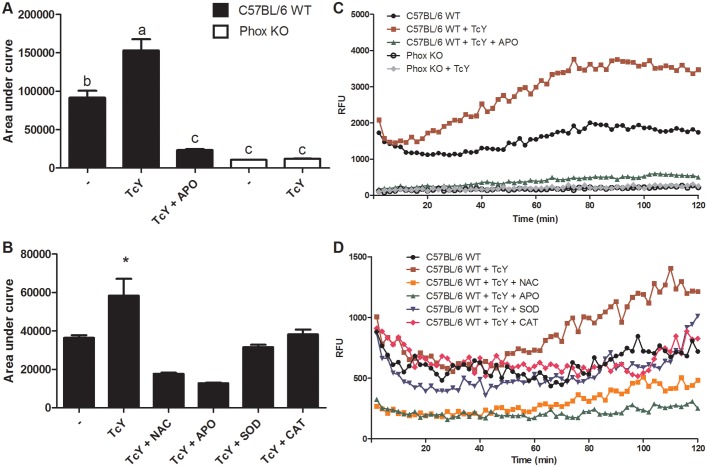
Fig 1. Production of reactive oxygen species by macrophages stimulated with Y strain of T. cruzi.
Thioglycolate-elicited macrophages were harvested from the peritoneal cavity of C57BL/6 WT and Phox KO mice 4 days after stimulation. Reactive oxygen species production by macrophages was detected by luminol. Macrophages previously incubated with apocynin (APO), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) for 2 hours were incubated with 0.5mM of luminol in culture medium and exposed to T. cruzi trypomastigotes. Chemiluminescence was continuously measured immediately after T. cruzi addition to the macrophage monolayer, and the area under the obtained curves was calculated. (A, C) Graphs showing area under curve, data represent mean of triplicates ± S.D. of total counts in 120 min. (B, D) Graphs showing chemiluminiscence rates, data represent means of triplicate counts in 120 min, standard deviations were omitted for clarity. The graphs are representative of five independent experiments performed in triplicate (cells were pooled from three mice for each replicate). * refers to significant differences from the infected non-treated macrophages. Bars marked by different letters are statistically different (p<0.05, one-way ANOVA test with Bonferroni post-test).