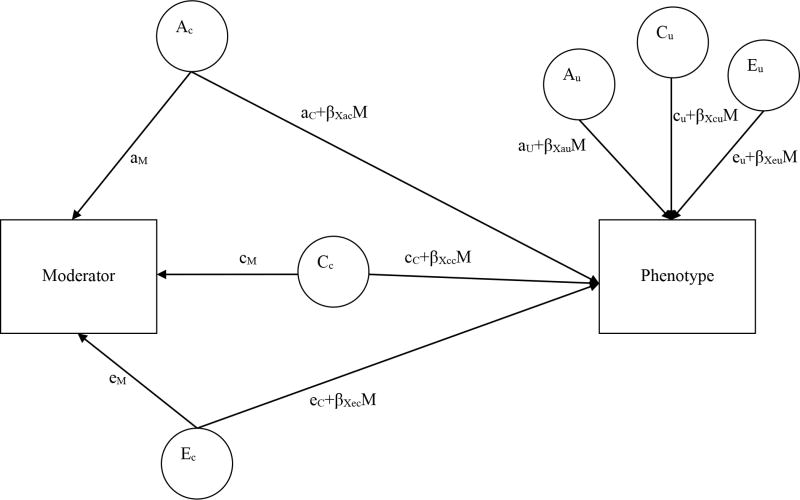
Figure 1.
Bivariate moderation model.
The model is shown for only one member of a twin pair. Genetic and environmental influences on the Outcome Variable vary by level of the Moderator Variable. A=additive genetics, C= shared environmental influences, and E=non-shared environmental influences. AC, CC, and EC are variance components underlying the Moderator that also influence the Outcome (i.e., “common components”), and AU, CU, and EU represent residual (“unique”) variance in the Outcome after accounting for the variance in common with the Moderator. β coefficients index the direction and magnitude of moderation. When all β coefficients are set to zero, this represents no moderation effects. Total phenotypic variance in the Outcome can be calculated by squaring and summing all of the paths leading to it: Var(Outcome) = (aC+βacM)2 + (aU+βauM)2 + (cC+βccM)2 + (cU+βcuM)2 + (eC+βecM)2 + (eU+βeuM)2.