Fig. 3.
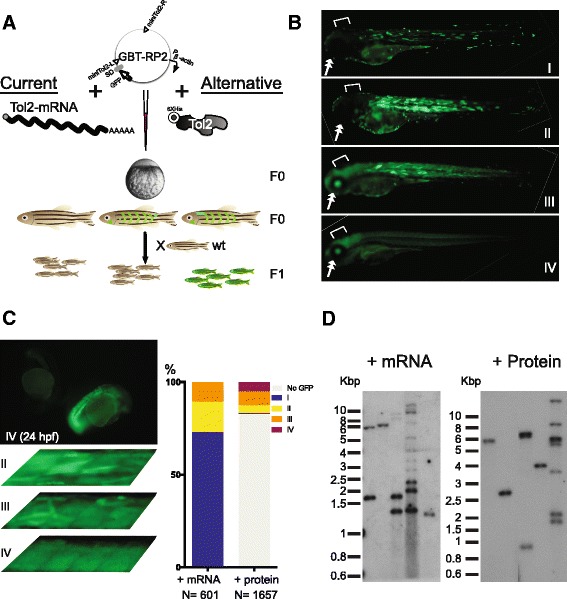
His-Tol2 is a fully functional transposase in vivo. a Diagram showing microinjection of zebrafish embryo at one-cell stage to generate transgenic animals. GBT-RP2 plasmid containing GFP-reporter gene trap was co-injected with either Tol2 mRNA or His-Tol2 protein. Mosaic somatic GFP signals were seen in F0 injected fish. F0 embryos were raised to adult and outcrossed to obtain F1 generation. Ubiquitous GFP would be detected in F1 fish if the integration was due to a gene trap event and was passed through the germline. Molecular analysis of transposon insertion numbers and genomic locations was carried out on tissue from F1 generation animals. Pβ-actin: β-actin promoter; SD: splice donor. b Representative images of F0 embryos demonstrating a catalog of GFP-positive somatic patterns that could be observed at 3 dpf from microinjections of different methods. Notice the signal difference in eyes (double arrow) and brain regions (open end arrow) for each category. With vector-only injections, notice only Cat. I and II patterns were observed. c A small number of His-Tol2 protein injected embryos showing ubiquitous whole body green fluorescence as early as 24 hpf. Those fish generally displayed uniform GFP expression throughout the body, with few uneven myotome GFP stripes at 3 dpf (Cat. IV). Also shown are 3 dpf injected fish somites at higher magnification, demonstrating the difference in uniformity of GFP signals in tissues from various injection categories. Injection GFP pattern distribution from typical RNA or protein mediated injection was shown. d GFP-positive F1 fish from either founder family generated by mRNA injection or His-Tol2 injection were subjected to fin-clip and Southern blot analysis with a GFP probe. Each lane represents one individual F1 adult fish. Southern blots from 5 adult fish selected from random founder family are shown for each method. See also Additional file 1
