Fig. 1.
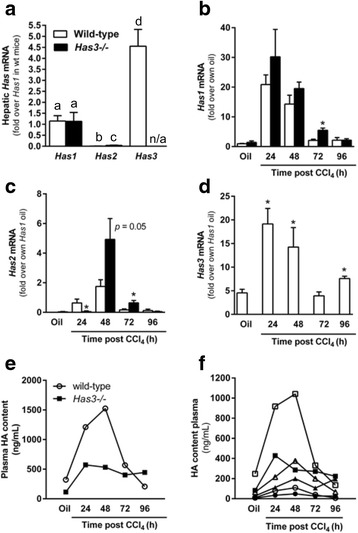
Hepatic Has enzymes and plasma HA levels in wild-type and Has3−/− mice. a Real-time PCR was used to measure basal levels of hepatic Has enzyme transcript accumulation in the wild-type and Has3−/− mice. Data were normalized to 18S and then expressed as fold change over wild-type hepatic Has1 content. Bars with different alphabetical superscripts are significantly different from one another (P < 0.05). b–d The mice were exposed to CCl4 and euthanized 24, 48, 72, or 96 h later. Control animals received an olive oil (oil) injection. Real-time PCR was used to measure hepatic Has1 (b), Has2 (c), and Has3 (d) in the livers from the wild-type and HAS3-deficient mice. *P < 0.05 when compared to the wild-type mice at the same time point. An ELISA-like assay (see the “Methods” section for details on this antibody-independent assay) was used to determine HA concentration in pooled plasma from the wild-type and Has3−/− mice either before (e) or after (f) HA fractionation using molecular weight cut-off columns. In e and f, the open symbols indicate wild-type mice while the closed symbols indicate Has3−/− mice. Circles indicate HA pools less than 100 kDa, squares indicate HA pools between 100 and 300 kDa, and triangles indicate HA pools greater than 300 kDa. Statistical analysis was not performed on these pooled samples. See Table 1 for additional details. n/a not applicable. N = 6–8 mice per experimental group
