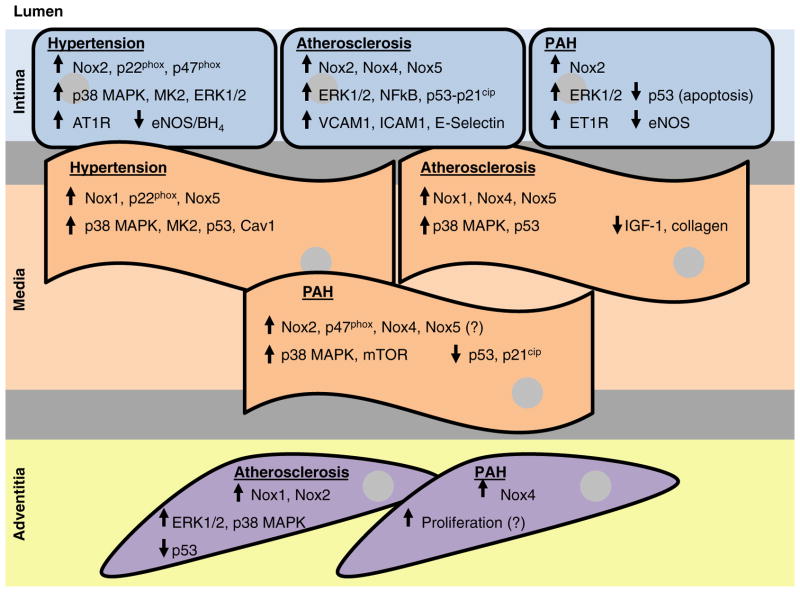
Figure 2. Effects of Nox-derived ROS on redox-sensitive longevity signalling in the vessel wall.
Summary of the effects of hypertension, atherosclerosis and PAH on age-related redox-sensitive signalling pathways linked to the different vascular cells comprising the vessel wall (intima: endothelial cells; media: VSMCs; adventitia: fibroblasts/myofibroblasts) as a consequence of Nox-derived ROS. Arrows depict either increased or decreased protein expression or signalling pathway activation. A question mark (?) depicts a potential effect wherein more conclusive evidence is required to fully support the observations in the literature.