Figure 2. Dexmedetomidine on bilateral mechanically and heat‐evoked paw withdrawal reflexes .
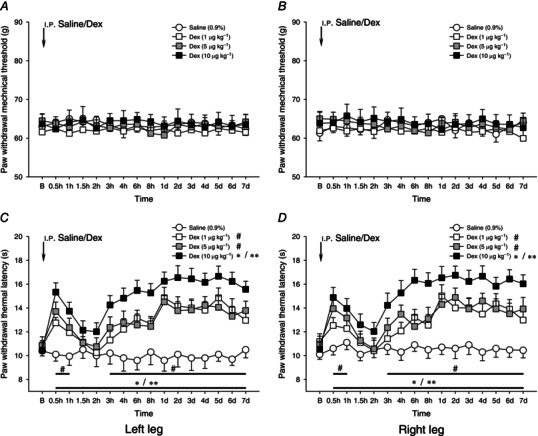
Effects of i.p. administration of dexmedetomidine (Dex, 1–10 μg kg−1) on bilateral mechanically (A and B) and heat (C and D) evoked paw withdrawal reflexes. Dex at a dose of 1–10 μg kg−1 failed to affect the mechanical paw withdrawal threshold. In contrast, Dex significantly prolonged the paw withdrawal heat latency in a bi‐phasic manner; there was a short‐term (around 1.5–2 h) prolongation of paw withdrawal heat latency, followed by a long‐term increase in heat latency lasting over 7 days (C and D). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 and # P < 0.05 compared with 0.9% saline injection (n = 10 for each group). B, baseline responses before the i.p. injection of 0.9% saline or Dex.
