Figure 1. Interplay between Shh and Ca2+ spike activity regulates neurotransmitter specification in developing spinal neurons.
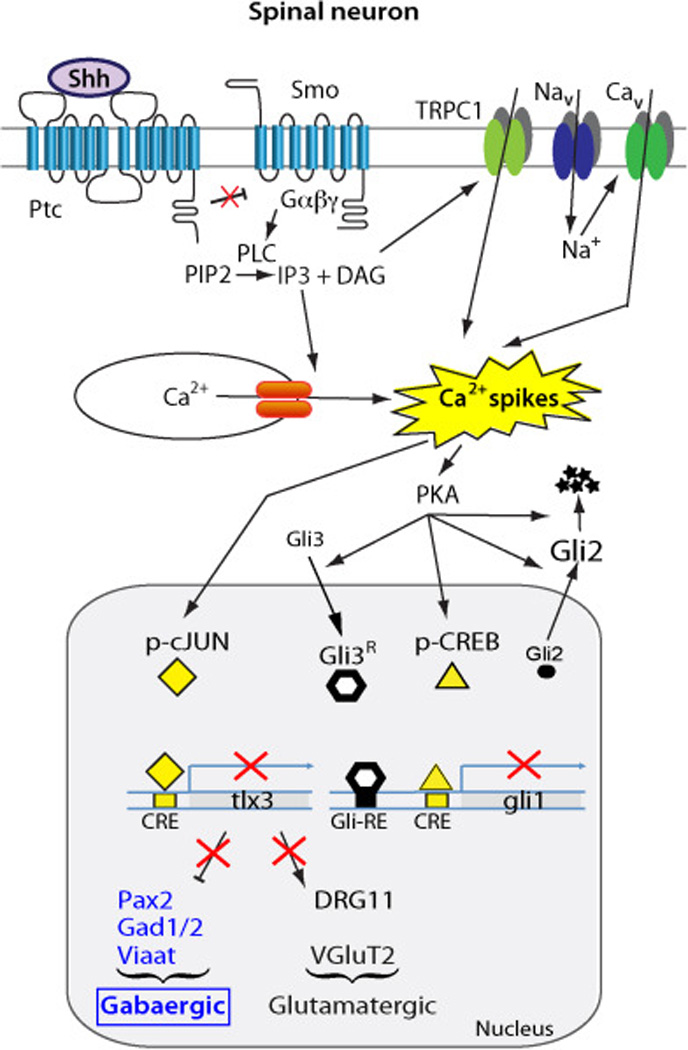
Shh binds to Patched (Ptc) releasing the constitutive inhibition on the coreceptor Smoothened (Smo) which activates phopholipase C (PLC) that increases inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) levels thus enhancing Ca2+ spike activity through the activation of transient receptor potential channel 1 (TRPC1), voltage-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels (Nav, Cav) and Ca2+ release from stores. Enhanced Ca2+ spike activity intercalates in Shh canonical pathway, inverting Shh action and leading to Gli2 cytosolic localization, Gli2 and Gli3 processing into repressor forms, repression of Gli1 transcription and an overall downregulation of Gli activity. In contrast, Ca2+ spikes activate transcription factors cAMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) and cJun, which promote the expression of the GABAergic over glutamatergic phenotype by regulating expression of the transcription factor selector tlx3. Based on Cheng et al., 2004, Marek et al., 2010, Belgacem and Borodinsky, 2011, 2015.
