Fig. 1.
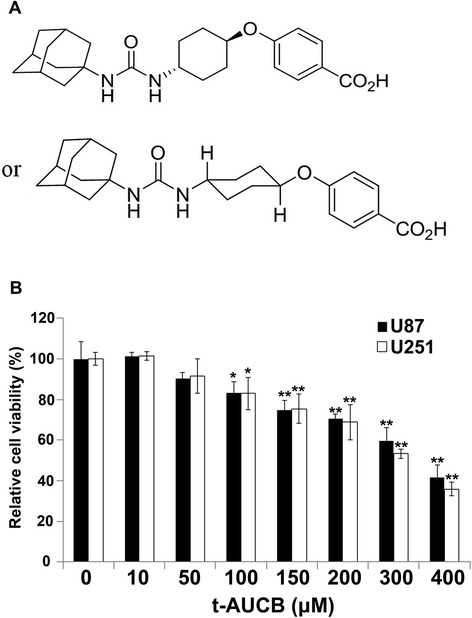
t-AUCB inhibits cell proliferation. a: The chemical constitution of t-AUCB. b: The percentage of OD value in t-AUCB treated cells compare with control represent the relative cell viability (%) in CCK-8 assay. U87 and U251 cells were treated with vehicle control (0 μM), 10 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM, 150 μM, 200 μM, 300 μM or 400 μM t-AUCB for 48 h. t-AUCB suppresses cell proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner since 100 μM (*P < 0.05). 150 μM to 400 μM t-AUCB causes more efficient cell growth inhibition (**P < 0.01)
