Figure 1.
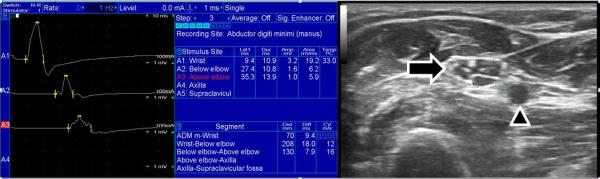
The ulnar motor nerve conduction study and ulnar nerve ultrasound in an individual with CIDP are depicted. The nerve conduction studies show a drop in amplitude when stimulation at the wrist is compared to the forearm. Since no median-ulnar anastomosis was detected, and similar amplitude drops were detected in other nerves, this is consistent with a conduction block. At the site of ulnar conduction block in the forearm the ulnar nerve cross-sectional area was greatly increased (28 mm2, indicated by arrow) compared with our reference range (normal < 10 mm2). Additionally, large fascicles can be seen within the nerve. The arrowhead points at the ulnar artery.