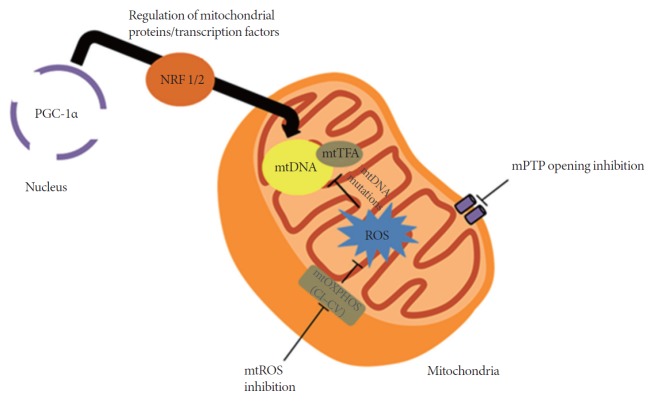
Fig. 1.
Selected examples of current methods in mitochondrial targeting. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), which is considered a master regulator of mitochondrial proteins and transcription factors, affects the expression of mitochondrial (mt)DNA. Inhibition of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) prevents damage to the mtDNA, decreasing the possibility of mutations. Opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) increases mitochondrial membrane permeability, causing further depolarization of the mitochondria, resulting in the loss of membrane potential. When this occurs, adenosine triphosphate production is severely affected and causes the heart to fail; thus the need to inhibit mPTP opening. CI–CV, complexes I–V of the mitochondria; mtOXPHOS, mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation; NRF 1/2, nuclear respiratory factor 1/2; mtTFA, mitochondrial transcription factor A.