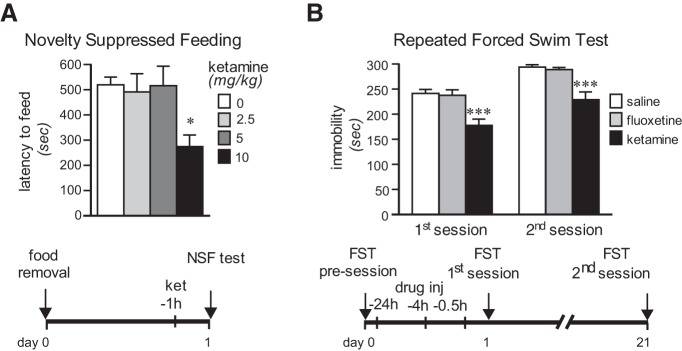
Figure 1.
Rapid and sustained behavioral effects of S-ketamine. A, Short-term S-ketamine (ket) treatment reduced the latency to eat in the novelty-suppressed feeding test (one-way ANOVA, F(3,14) = 6.61, p = 0.005; *Holm–Sidak test, 10 mg/ml vs saline, p = 0.004). B, In the repeated forced swim test, short-term administration of S-ketamine reduced the time spent immobile immediately and 21 d later, while fluoxetine had no effect (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA; treatment effect: F(2,9) = 31.65, p = 0.0001; time effect: F(1,9) = 31.47, p = 0.0003; treatment × time interaction: F(2,9) = 0.002, p =0.99; ***p < 0.001 vs saline in post hoc test). All bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).