Fig. 7.
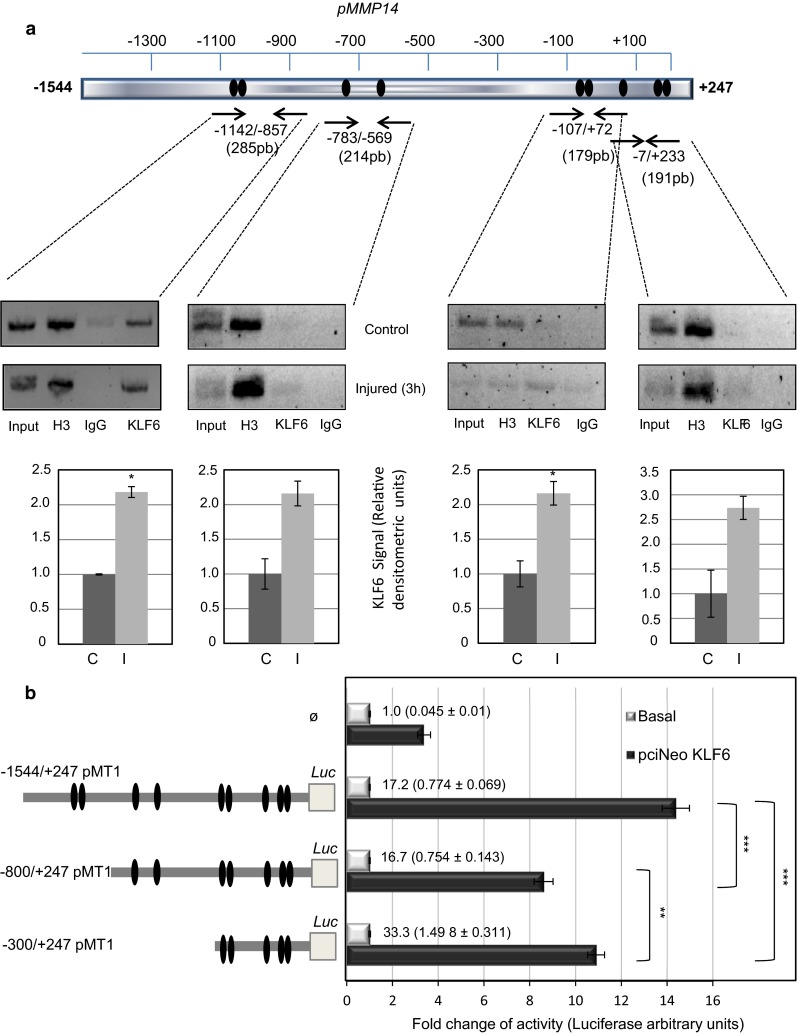
KLF6 interacts with MMP14 gene promoter and regulates its activity. a KLF6 interacts with MMP14 promoter in HUVECs. In silico analysis revealed the presence of potential KLF6-binding sites (black ovals) within GC-rich domains on MMP14 gene promoter using Genomatix MatInspector software (scheme in upper panel). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments of KLF6 over the 5′-proximal MMP14 promoter were carried out in HUVECs comparing control condition and after 3 h of wound healing (middle panel). The chromatin was digested obtaining a 150–300-bp fragments-enrichment. Immunoprecipitation was carried out with anti-KLF6, anti-H3K4 (positive control) and non-immune (IgG) antibodies. PCRs were done with primers to detect four regions containing putative KLF6-sites in the promoter region of MMP14, using the total lysate as an input of the sample. KLF6 binding to the different pMMP14 regions from the ChIP experiment was measured by densitometry of the individual bands, and values of the (KLF6-IgG)/Input ratios were represented (bottom panel). Normalized ratios in basal conditions (C) and 3 h after the endothelial injury (I) are shown. b KLF6 transactivates the MMP14 promoter. Left 5′-deleted construct series of the MMP14 promoter cloned into pGL2-luc. The size of each construct compared with the size of the whole promoter construct is shown in the scheme. The drawing is not to scale. Right HEK293T was co-transfected with a luciferase reporter driven by different MMP14 promoter constructs in pGL2-luc (−1544/+247 pMT1; −800/+247 pMT1; and −300/+247 pMT1) which include different putative binding GC-rich motifs for KLF6, and the expression vector pCIneo-KLF6. The pGL2-Luc empty vector (Ø) was used as a negative control. Overexpression of KLF6 upregulates between 8 and 14 times the activities of the MMP14 promoter constructs. The relative promoter activity under basal conditions is indicated in the corresponding bars, and the actual values of luciferase activity are shown in parenthesis. Transfection efficiency was corrected by relating luciferase activity to β-galactosidase activity. Results are expressed as a fold induction with respect to the basal activity of the corresponding constructs (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001)
