Figure 7. Overview of one- (radical) and two-electron (molecular) reactions of amino acid-, peptide- and protein-hydroperoxides (highlighted in blue).
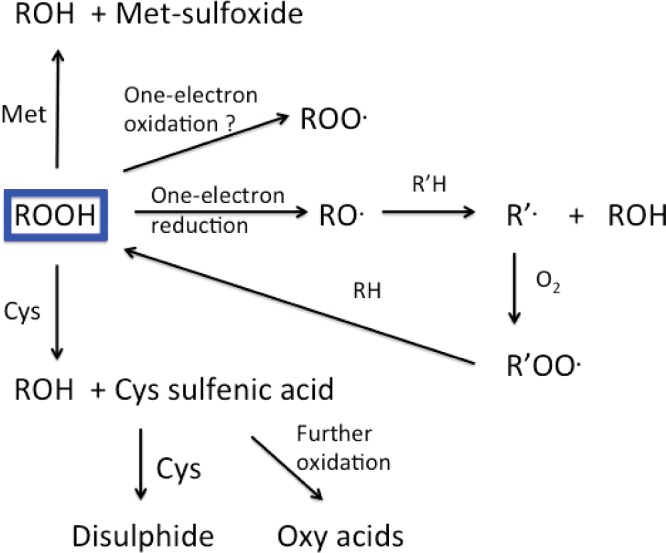
The two-electron reactions occur predominantly with Cys residues to give sulfenic acids, disulfides, and higher oxy acids. Reaction has also been reported for Met, some disulfides such as lipoic acid (not shown) and selenium-containing compounds, including selenomethionine and selenocysteine (Sec)-containing enzymes such as thioredoxin reductase and glutathione peroxidase (not shown). One-electron reduction yields alkoxyl radicals and further oxidation reactions (for further details of specific mechanisms see Figure 8), whereas one-electron oxidation may yield peroxyl radicals; the latter process is poorly characterized.
