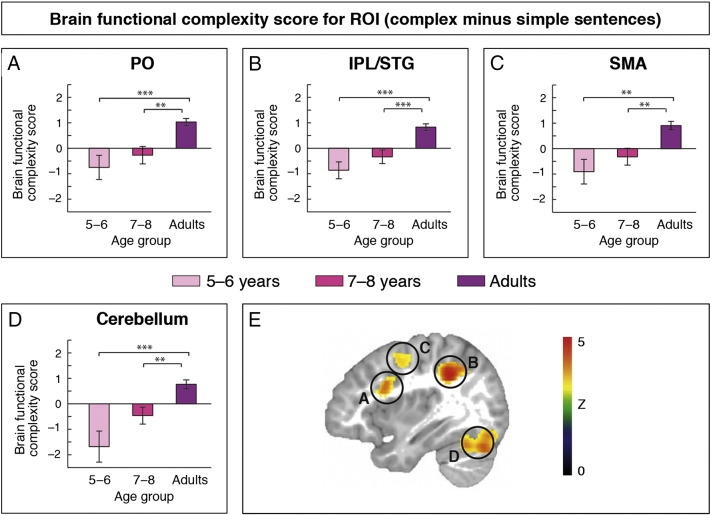
Fig. S5.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging results. Whole-brain results (p < 0.001, corrected) reveal interactions between age and sentence complexity in left pars opercularis (PO), left inferior parietal lobe extending into the posterior superior temporal gyrus (IPL/STG), bilateral supplementary motor area (SMA), and bilateral cerebellum. Planned comparisons in each region of interest (ROI; A–D) on functional complexity scores (i.e., percent single change for simple sentences subtracted from percent signal change for complex sentences; p < 0.01, corrected) indicate increased functional selectivity for syntactic complexity with age for all ROIs. (E) Neuroanatomical location of the ROIs.