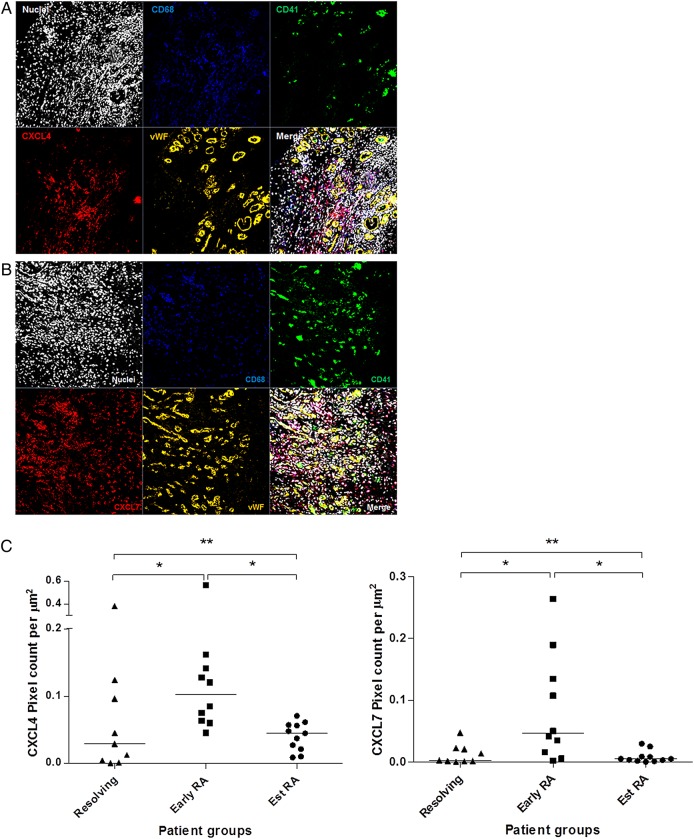
Figure 3.
Immunofluorescence staining of CXLC4 and CXCL7 in synovial tissue sections. (A) Synovial tissue staining of CXCL4 (red), CD68 (blue), CD41 (green) and von Willebrand factor (vWF) (orange). (B) Synovial tissue staining of CXCL7 (red), CD68 (blue), CD41 (green) and vWF (orange). Nuclear counterstain is shown. Images are representative of early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium (n=10). No staining was observed using isotype and concentration-matched negative controls. Images were taken at ×40 magnification. (C) Quantification of CXCL4 and CXCL7 staining, calculated as the number of pixels per μm2 over 6× 2×2 tile scans at ×40 magnification, in synovial tissue sections from patients with resolving arthritis (n=9), early RA (n=10) and established RA (n=11). Patients with early RA showed a significantly higher level of CXCL4 (p<0.05) and CXCL7 (p<0.05) compared with patients with resolving arthritis and established RA. Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn's post-test; * p<0.05, ** p<0.01.