Figure 2.
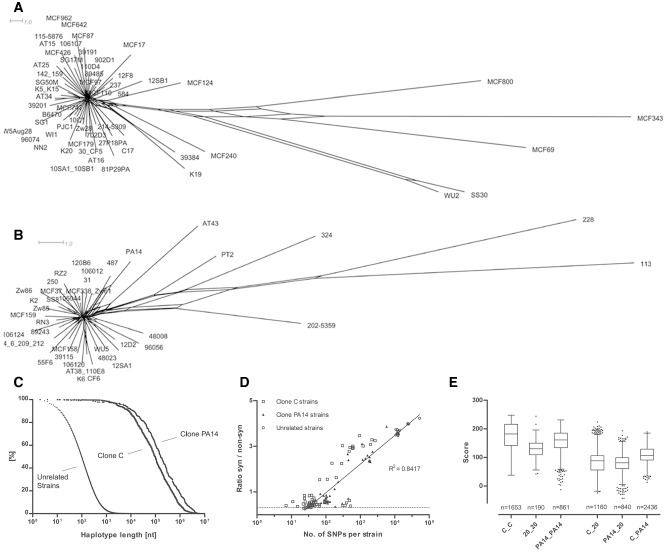
Intraclonal genome diversity of the clonal complexes C and PA14.
A and B. SNP‐based phylogenetic trees of the clonal complexes C (A) and PA14 (B).
C. Conservation of the core genome. Normalized distribution of the length of 100% pairwise conserved sequence (‘haplotype’) in 58 clone C (n = 33 800 haplotypes), 42 clone PA14 (n = 9510) and 20 clonally unrelated P. aeruginosa strains (n = 3 779 224).
D. Comparison of intraclonal versus. interclonal sequence diversity: Plot of the ratio of synonymous to non‐synonymous SNPs versus the total number of SNPs per strain. Clone C, clone PA14 and clonally unrelated strains (reference: strain PAO1 genome) are differentiated by symbol. The dotted line indicates the expectancy value of random mutation.
E. Diversity of the accessory genome. Box‐plot presentation of the similarity of the accessory genome within and between clonal complexes. For each strain, a global score of relatedness was evaluated, whereby the two strains were assessed of whether they were concordant (assigned value: +1) or discordant (assigned value: −1) for the presence or absence of each RGP or genomic island known from eight completely sequenced P. aeruginosa genomes (PAO1, PA14, PACS2, PA7, LESB58, C3719, 2192). Please note the large overlap of scores of the intraclonal comparisons (C_C; PA14_PA14) with those of interclonal comparisons of 20 unrelated strains (20_20).
