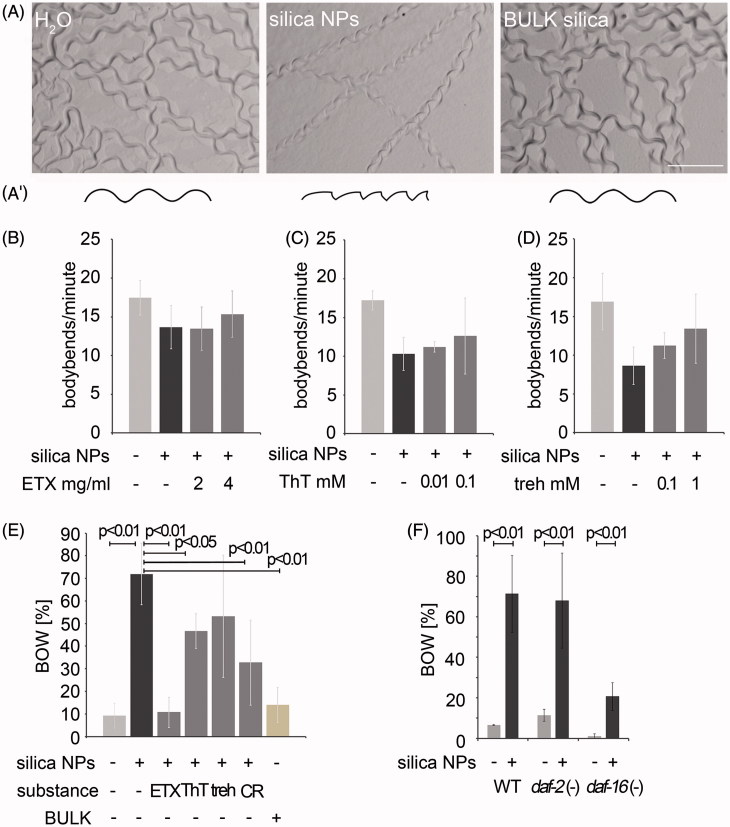
Figure 3.
Cellular pathway validation by behavioral phenotyping. (A) Micrography of representative forward locomotion tracks on agar plates of 2-day-old, adult wild type C. elegans that were mock (H2O)-treated or exposed to silica NP, or BULK silica for 24 h (A′) Schematic of the tracks showing that the H2O- and BULK silica-treated worms crawl in sinusoidal curves, whereas silica NP-treated worms move in a serrated pattern. (B–D) Quantification of the locomotion by body bend counts per minute of 2-day-old, adult wild type C. elegans that were treated with H2O, silica NPs or silica NPs in combination with different concentrations of inhibitors of amyloid formation for 24 h: (B) ethosuximide, (C) thioflavin T and (D) trehalose. Values represent means ± SD from four independent experiments with n ≥ 17 for each treatment. (E) Ratio of the internal hatch/bag of worms (BOW) phenotype in a population of 2-day-old, adult wild type C. elegans that were treated for 26 h with H2O, silica NPs, BULK silica or silica NPs in combination with ethosuximide, thioflavin T, Congo red or trehalose in liquid medium. Silica NP-treated worms show an increase of the BOW-phenotype that is fully rescued by ethosuximide. Values represent means ± SD from at least three independent experiments with n > 100 for each treatment (H2O; ethosuximide/silica NPs; Congo red/silica NPs; BULK silica versus silica NPs, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test p < 0.01; thioflavin T/silica NPs versus silica NPs, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test p < 0.05). (F) Ratio of the BOW-phenotype in a population of 2-day-old, adult wild type C. elegans compared with long-lived daf-2 mutants or short-lived daf-16 mutants that were treated for 26 h with H2O, silica NPs. Values represent means ± SD from four independent experiments with n > 170 for each genotype and treatment (H2O versus silica NPs, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test p < 0.01). BOW, bag of worms; CR, Congo red; ETX, ethosuximide; ThT, thioflavin T; treh, trehalose.