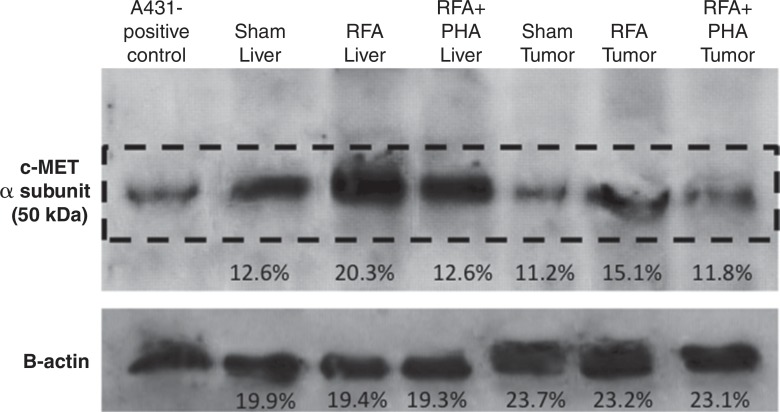
Figure 3c:
Hepatic RF ablation (RFA) increases periablational and distant tumor c-Met receptor expression. (a, b) c-Met expression is increased in periablational rim in normal liver after RF ablation compared with sham treatment. Immunohistochemical staining for c-Met receptor expression demonstrates a rim of increased c-Met staining around ablation zone (arrowheads) after RF ablation of normal liver. No changes were observed at site of sham treatment (ie, electrode placement in liver). (c) Liver RF ablation–induced changes in local and distant c-Met without and with PHA. Western blot assays demonstrate increased c-Met receptor protein in tissue harvested from periablational tissue surrounding liver ablation zone compared with sham treatment (seen as dense bands after gel electrophoresis at 50-kDa level, where c-Met receptor α subunit is expected, after β-actin standardization) (20.3% vs 12.6%, respectively). c-Met receptor protein levels are also slightly increased in distant tumor after hepatic RF ablation compared with sham treatment (15.1% vs 11.2%, respectively). β-actin levels were similar for all arms, which confirms increases in observed c-Met receptor expression. (d) Liver RF ablation–induced changes in local c-Met with and without implanted distant c-Met–positive or negative tumor. Western blot assays demonstrate increased periablational c-Met expression after hepatic RF ablation in all arms, regardless of whether there was any distant tumor present (24.1% vs 24.6%) or whether distant tumor expressed the c-Met receptor (24.6% vs 23.9%).