Figure 5.
The Common Progenitor Activity Is Located within the MHCIIhi Fraction of Ly-51+PLET1+ TECs
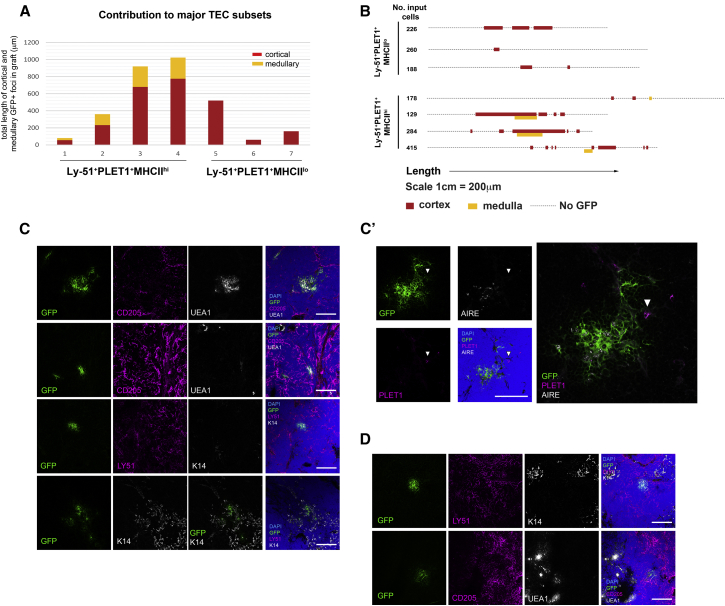
(A) Graph shows contribution of test cells of the phenotypes shown to cortical and medullary TEC sublineages. x axis indicates individual grafts. y axis indicates total length of all cortical (red) and medullary (yellow) GFP+ foci in a particular graft, in micrometers. MHC class IIhiLy-51+PLET+ TECs can contribute to both cTEC and mTEC sub-lineages while MHC class IIlo/negLy-51+PLET1+ TECs can contribute only to cTECs.
(B) Schematic representation showing distribution of GFP+ cells in grafts seeded with cells of the phenotypes shown. The dotted line represents the total length of the graft (1 cm represents 200 μm), for each graft, the whole graft was sectioned and each section was analyzed for the presence of GFP+ regions and the localization of the GFP+ areas to cortex and/or medulla. For the purpose of representation, information from the y and z planes are collapsed onto the x axis. Where contribution of GFP+ cells to cortical and medullary regions overlaps in this schematic, these regions were contiguous in most but not all cases.
(C, C’, and D) Images show immunohistochemical analysis of grafts derived from the MHCIIhiLy-51+PLET1+ input TEC (C and C’) and MHCIIlo/negLy-51+PLET1+ (D) populations after staining with markers indicative of defined cortical and medullary TEC populations, as shown. MHCIIhiLy-51+PLET1+ input TECs, n = 4; MHCIIlo/negLy-51+PLET1+, n = 3. Images show representative data from three of four independent grafts for MHCIIhiLy-51+PLET1+ and two of three independent grafts for MHCIIlo/negLy-51+PLET1+input TECs. Arrowhead in (C′) indicates GFP+PLET1+ cell.
See also Table S2.