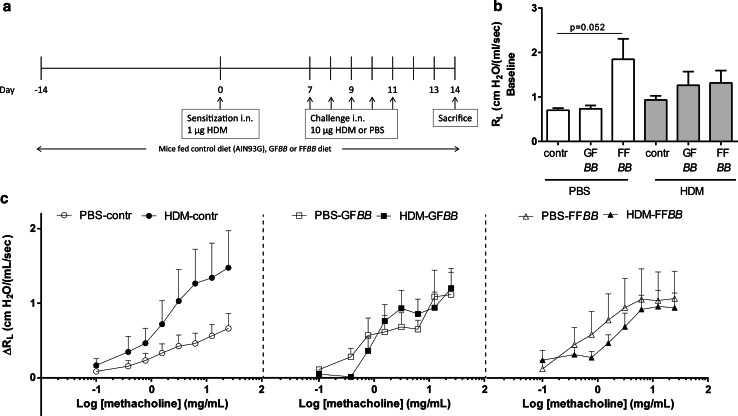
Fig. 1.
Treatment protocol of the allergic house dust mite (HDM) asthma model and lung resistance measurement. Male BALB/c mice were sensitized intranasally (i.n.) with HDM on day 0 and were challenged i.n. for five consecutive days with HDM or PBS. Mice were fed the control diet (AIN93G, contr), a diet containing a 1 % w/w 9:1 mixture of GOS and long-chain fructo-oligosaccharide (GF) or 1 % w/w 1:1 mixture of short-chain fructo-oligosaccharide and long-chain fructo-oligosaccharide (FF) both in combination with 2×10E9 colony-forming units/g Bifidobacterium breve M-16V (BB) (2 % w/w). The GFBB and FFBB interventions started 2 weeks prior to sensitization and continued during the entire experiment. All mice were killed on day 14 (a). Basal airway resistance (RL) (b) and ΔRL after baseline correction in response to increasing doses of methacholine were measured on day 14 (c). HDM–PBS: HDM-sensitized and PBS-challenged mice (white bars), HDM–HDM: HDM-sensitized and HDM-challenged mice (gray bars), Contr: control diet, GFBB: mixture of GOS and long-chain fructo-oligosaccharide with Bifidobacterium breve M-16V diet, FFBB: mixture of short-chain fructo-oligosaccharide and long-chain fructo-oligosaccharide with Bifidobacterium breve M-16V diet