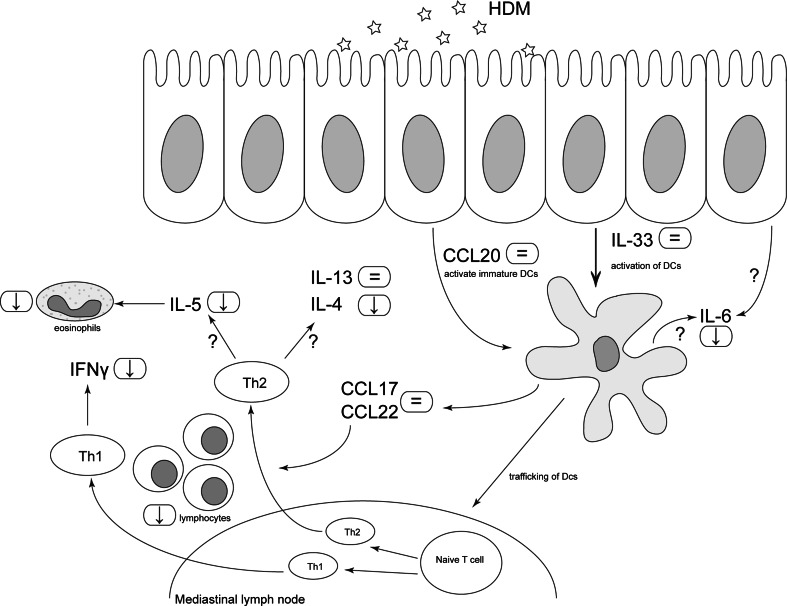
Fig. 6.
Overview of the effects of the synbiotic diet FFBB. After the initial exposure to HDM, CCL20 is secreted by the airway epithelium, which will activate immature DCs. IL-33, also secreted by the epithelium, activates the DCs. Both CCL20 and IL-33 concentrations in lung homogenate supernatants were not affected by the FFBB diet. Activated DCs secrete CCL17 and CCL22, which are chemo-attractants for Th2 cells, and will traffic to the mediastinal lymph nodes to differentiate naïve T cells into Th2 cells. The FFBB diet did not affect CCL17 and CCL22 release by these DC. In contrast, IL-6, which can be secreted by lung epithelial cells or inflammatory cells such as DC, was suppressed which correlated with the reduced inflammatory cell influx. Mainly lymphocyte and eosinophil influx was lowered by the FFBB diet. Among other cells, Th2 cells secrete IL-13, IL-4 and IL-5 and Th1 cells secrete IFN-γ. Although IL-13 remained high, the FFBB diet reduced IL-4 and IFNγ. Furthermore, FFBB tended to suppress IL-5 levels which correlated with the reduced number of lymphocytes and eosinophils upon dietary intervention