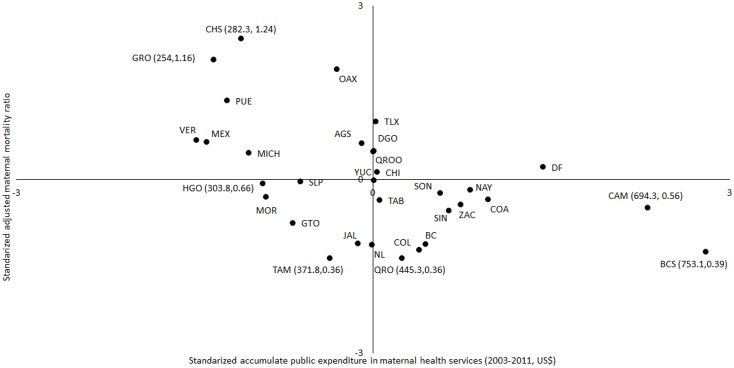
Fig 4. Performance of Mexican states in Maternal Health: Public expenditure and maternal mortality/antenatal care coverage results.
Note: In parenthesis absolute values. Maternal mortality was based on the WHO Guidelines for the implementation of the International Classification of Diseases to the deaths during pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum (37), and includes two types of maternal deaths: First, deaths during pregnancy or within 42 days following the end of the pregnancy, regardless of the length and location of the pregnancy, due to any cause related to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes; and, Second, deaths occurred from direct or indirect causes more than 42 days but less than one year after termination of pregnancy (or late maternal deaths). Both in a given year, per 100 thousand live births in that same year and per percentage point of adequate ANC coverage. *Adequate ANC (timely, ≥4 ANC visits + content of ANC ≥75% of basic procedures) were estimated using non-linear regression models (logit) adjusted by all population and contextual characteristics mentioned in Table 1. **Expressed in US$ and per women 15–49 years of age (at constant prices of 2011).