Figure 3. CHL1CTFβ Fragment and Its ERM Recruitment Domain Are Required for Sema3A-Induced Growth Cone Collapse in Thalamic Neurons.
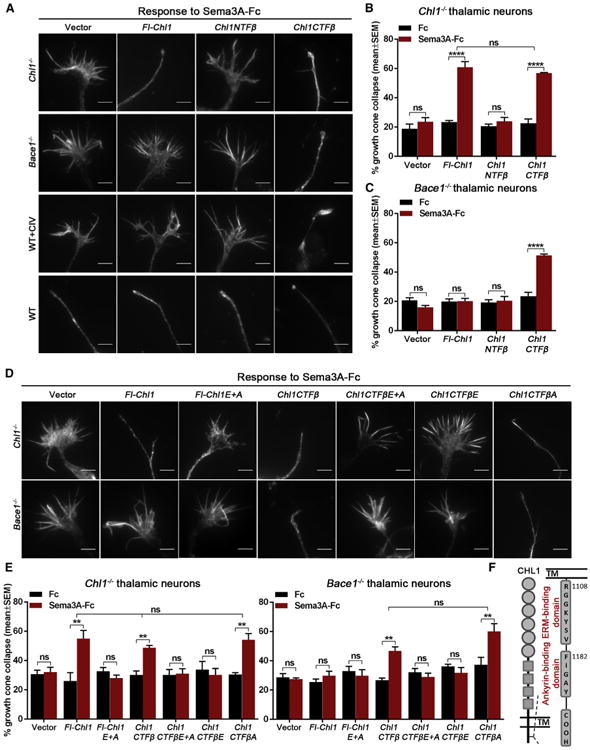
(A) Representative images of Chl1−/−, Bace1−/−, BACE1 inhibitor-treated (1 μMCIV), and WT growth cones co-transfected with GFP and empty vector, Fl-Chl1, Chl1NTFβ, or Chl1CTFβ in response to 5 nM Sema3A-Fc.
(B and C) Quantification of Sema3A-induced growth cone collapse in Chl1−/− (B) and Bace1−/− thalamic neurons co-transfected with empty vector, Fl-Chl1, Chl1NTFβ, or Chl1CTFβ (C).
(D and E) Analysis of Sema3A-induced growth cone collapse in Chl1−/− and Bace1−/− thalamic neurons co-transfected with GFP and empty vector, Fl-Chl1, CHL1 ERM and ankyrin double mutant (Fl-Chl1 E+A), Chl1CTFβ, CHL1CTFβ ERM and ankyrin double mutant (Chl1CTFβE+A), CHL1CTFβ ERM (Chl1CTFβE), or CHL1CTFβ ankyrin (Chl1CTFβA).
(F) Schematic representation of CHL1 C-terminal ERM- and ankyrin-binding sites.
Results are presented as mean ± SEM. The scale bars represent 5 μm. See also Figure S3.
