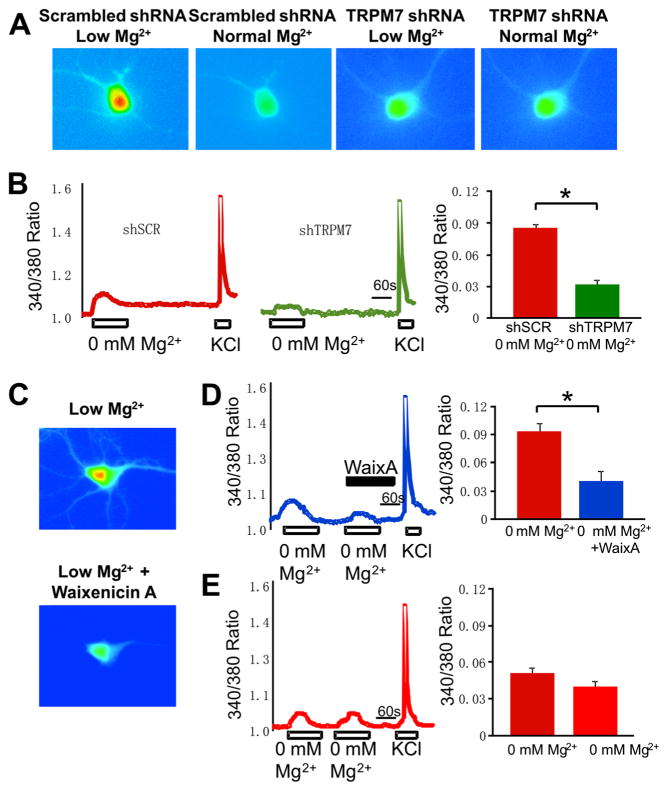
Fig. 6.
Calcium influx through TRPM7 is reduced in TRPM7 knockdown and waixenicin A-treated neurons. a Representative calcium images show that Mg2+-free and low Ca2+ application induce a smaller Ca2+ influx in TRPM7 shRNA transduced neurons than in neurons treated with scrambled shRNA. b Representative 340/380 ratio traces of neurons transduced with scrambled shRNA (left panel) or TRPM7 shRNA (middle panel); average peak 340/380 ratio values of TRPM7-induced calcium influx (right panel). c Representative images of control and waixenicin A-treated neurons. d Representative 340/380 ratio trace of neurons perfused with Mg2+-free solution followed by Mg2+-free solution together with 500 nM waixenicin A (left panel); average peak 340/380 ratio values of TRPM7-induced calcium influx (right panel). e Representative 340/380 ratio trace of two consecutive applications of Mg2+-free solution to hippocampal neurons (left panel) and average peak 340/380 ratio values of TRPM7-induced calcium influx (right panel). For scrambled shRNA neurons n=16, TRPM7 shRNA neurons n=16, untreated neurons n=10, waixenicin A-treated neurons n=10, control neurons n=19. Data are presented as mean±SEM. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc; *p<0.05