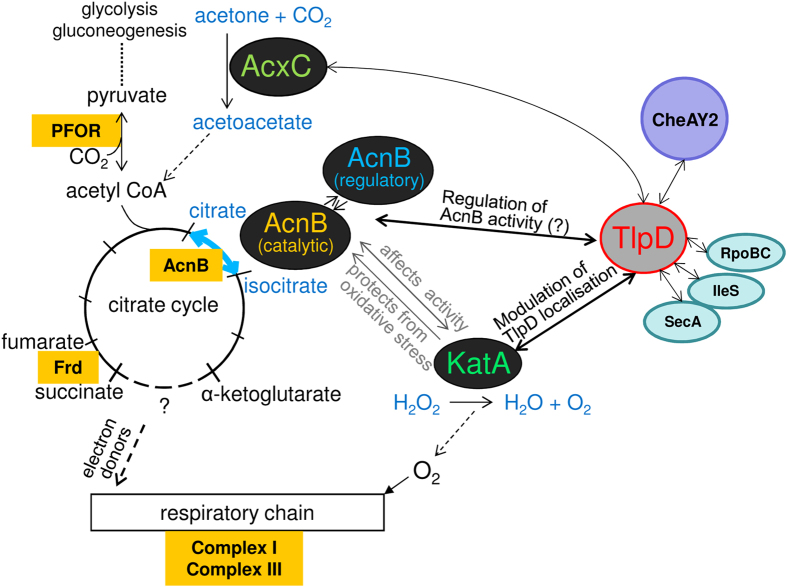
Figure 7. Model of protein-protein interactions of the H. pylori energy sensor TlpD and their connection to metabolism and gene regulation.
Several novel TlpD protein-protein interactions were identified in the present study (KatA, AcnB, CheAY2, IleS, RpoBC, SecA). This model depicts how some of these proteins, jointly with TlpD, integrate into the network of H. pylori metabolism and energy-related functions, which may feed back into TlpD-mediated energy sensing. AcnB is a bifunctional enzyme of the TCA cycle, converting citrate into isocitrate and vice versa. In H. pylori, microaerobic metabolism is thought to favour the generation of citrate by AcnB, feeding into CO2 fixation and gluconeogenesis53. KatA80 detoxifies H2O2 and oxygen radicals, and might thereby protect metabolic enzymes containing iron-sulfur clusters such as AcnB. The putative interactor AcxC is a subunit of acetone carboxylase54, which synthesises acetoacetate, an important precursor of the gluconeogenesis and TCA cofactor acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR), an iron-sulfur enzyme essential for the microaerobic, capnophilic metabolism of H. pylori51,52, can also govern the direction of metabolic flow in H. pylori from the citrate cycle to gluconeogenesis by CO2 fixation and pyruvate generation. By repleting acetyl-CoA, acetone carboxylase also supplements the PFOR reaction and gluconeogenesis. Under conditions of oxidative stress, AcnB switches between a catalytic and a regulatory function75. TlpD may interfere with AcnB activity and influence regulatory functions of AcnB under stress conditions. KatA possibly protects AcnB from oxidative stress to maintain AcnB catalytic function under oxidative conditions. Proteins containing iron-sulfur clusters46 which are integrated into this part of the metabolic network and may influence TlpD sensing under oxidative or metabolic stress (AcnB, fumarate reductase Frd, PFOR, and subunits of the respiratory complexes I and III) are highlighted by orange colour. Verified interactions between proteins are indicated by bold arrows. Additional potential interactors of TlpD whose direct interaction has not yet been clarified (SecA, IleS, RpoBC) are depicted for completeness.