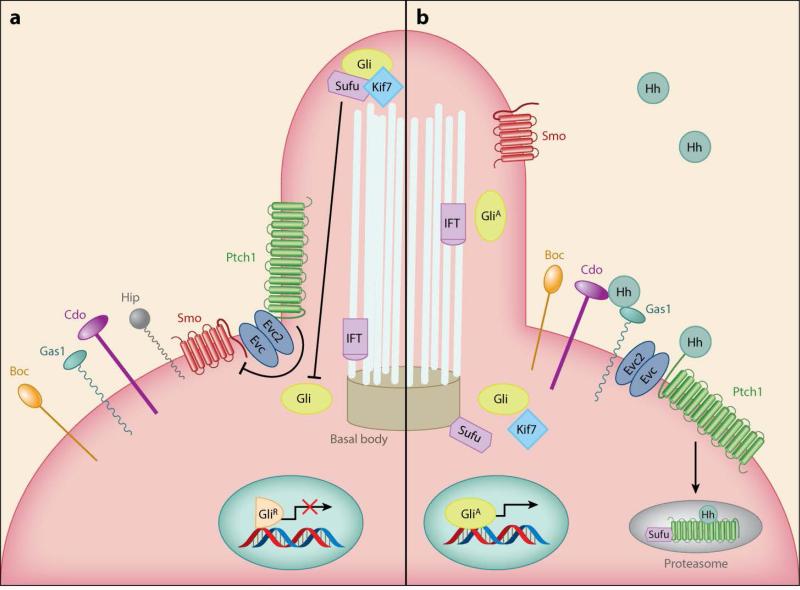
Figure 1.
The Hh signaling pathway. (a) Ptch1 is located at the base of the primary cilium, where it inhibits Smo. Gli transcription factors are found in the repressor form (GliR) in the cilium. Sufu can therefore complex with Gli proteins and inhibit their nuclear localization and transcriptional activity. (b) Upon Hh ligand binding, Ptch1 releases its repression, and Smo stimulates the accumulation of Gli factors in the active form (GliA), which can promote the transcription of Hh pathway target genes. Abbreviations: Boc, brother of Cdo/biregional Cdon-binding protein; Cdo, Cell adhesion molecule–related/downregulated by oncogenes; Evc2, Ellis van Creveld syndrome protein 2; Gas1, Growth arrest specific 1; Gli, Glioma-associated oncogene; Hh, Hedgehog; Hip, Hedgehog-interacting protein; Kif7, Kinesin family member 7; IFT, intraflagellar transport; Ptch1, Patched 1; Smo, Smoothened; Sufu, Suppressor of Fused.