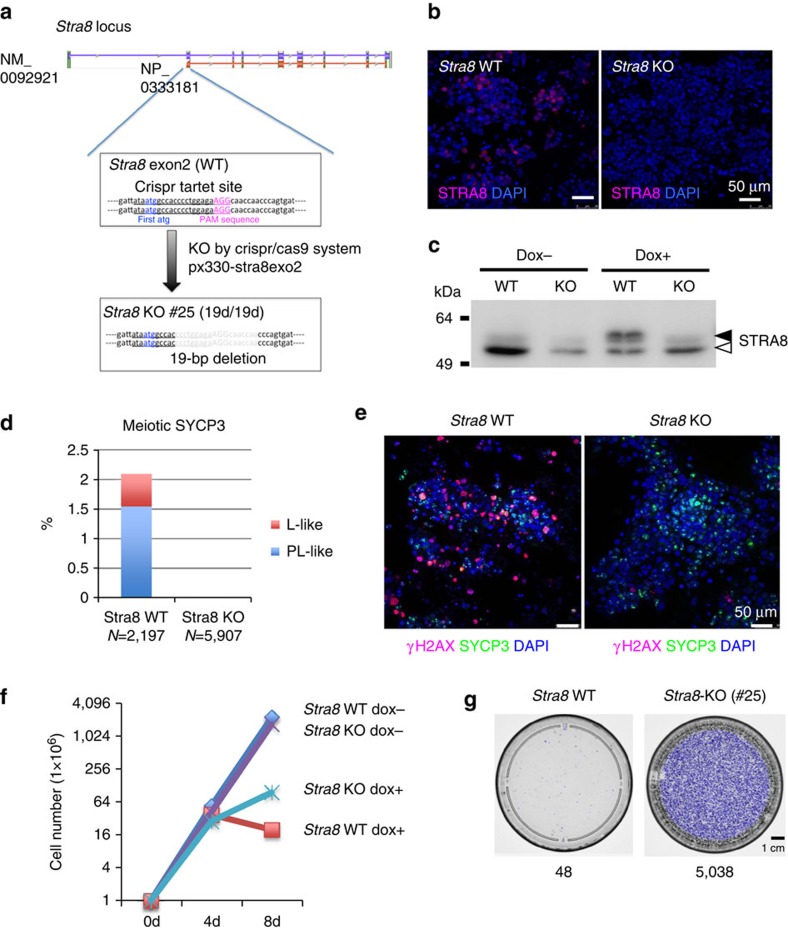
Figure 4. Induction of the Max expression ablation-mediated meiosis-like SYCP3-staining pattern in ESCs depends on the presence of a functional Stra8 gene.
(a) Schematic representation of CRISPR-Cas9-mediated disruption of the Stra8 gene. Genomic analyses revealed that Stra8 KO #25 clone had an out-of-frame mutation in both loci of the Stra8 gene due to homozygous deletion of 19 base pairs located immediately downstream of the ATG initiation codon in exon 2 of the gene. (b) Confirmation of the absence of functional Stra8 genes in the Stra8 KO #25 Max-null ESC clone. The Stra8 KO #25 clone and parental Max-null ESCs were treated with Dox for 9 days and then subjected to immunocytochemical analyses with an antibody against STRA8. (c) Western blot analyses of STRA8 in Stra8 KO #25 clone and parental Max-null ESCs cultured in the presence or absence of Dox. Solid and open arrowheads indicate specific and non-specific bands, respectively. (d) Frequency of preleptotene-, leptotene- and zygotene-like staining patterns in the Stra8 KO #25 clone and parental Max-null ESCs treated with Dox for 9 days. (e) Immunostaining analyses of γH2AX and SYCP3 in the Dox-treated (9 days) Stra8 KO #25 clone and parental Max-null ESCs. (f) Increase in the recovery of viable Dox-treated Max-null ESCs due to homozygous knockout of the Stra8 gene. The number of cells at day 0 was arbitrarily set to one. (g) Max-null ESCs (1 × 105) with or without functional Stra8 genes were individually transferred to 10-cm dishes and treated with Dox for 12 days. The cells were then subjected to Leishman's staining. Numbers under the dishes are the number of stained cell colonies. d, day; KO, knockout; WT, wild type.