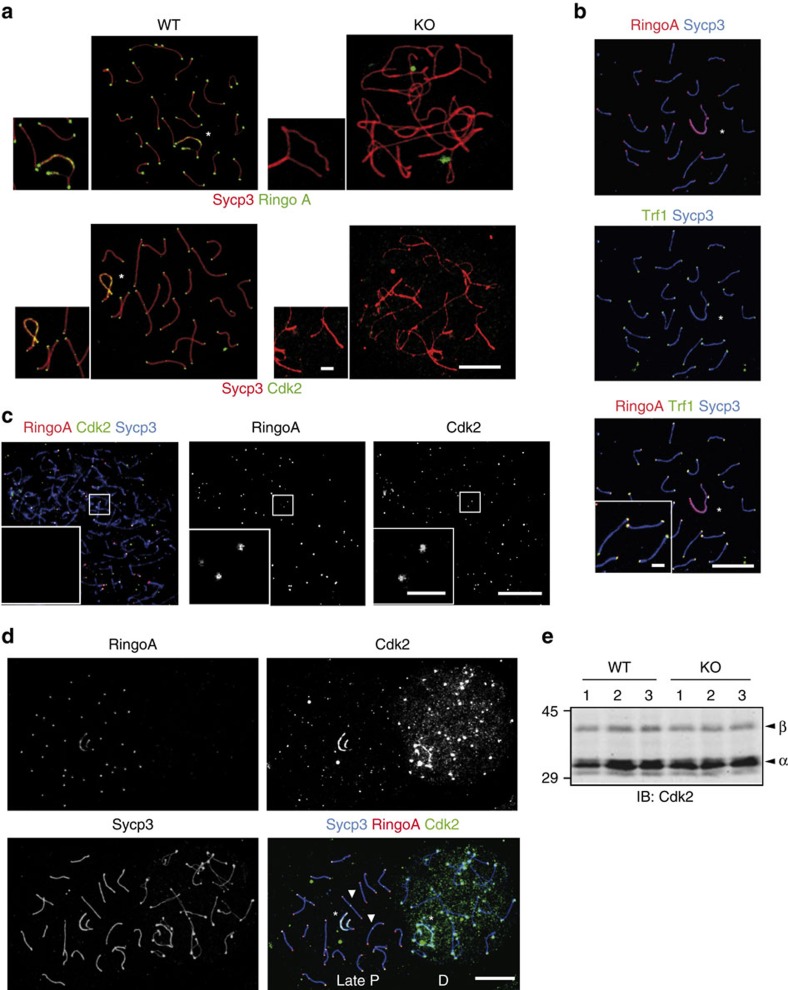
Figure 4. RingoA is required for Cdk2 localization and co-localizes with Cdk2 at telomeres in prophase I spermatocytes.
(a) WT and KO spread spermatocytes were immunolabelled for Sycp3 (red) and either RingoA (green) or Cdk2 (green). In WT pachytene spermatocytes, RingoA localizes at telomeres and the axial elements of sex chromosomes (star). Cdk2 localization at telomeres, the axial elements of sex chromosomes (star), and at late-recombination nodules is completely lost in KO spermatocytes. RingoA and Cdk2 are not detected in KO pachytene-like spermatocytes. (b) WT pachytene spread spermatocytes were immunolabelled for Sycp3 (blue), RingoA (red) and Trf1 (green). RingoA co-localizes with Trf1 at telomeres. (c) WT leptotene spread spermatocytes were immunolabelled for Sycp3 (blue), RingoA (red) and Cdk2 (green). Cdk2 and RingoA co-localize at the telomeric regions. (d) WT late pachytene and diplotene spermatocyte spreads were immunolabelled for Sycp3 (blue), RingoA (red) and Cdk2 (green). RingoA and Cdk2 co-localize until late pachytene. RingoA is absent upon entry into diplotene, while Cdk2 signal gets more dispersed within the nucleus. (e) Testis lysates from 18 dpp WT (n=3) or RingoA KO (n=3) mice were analysed by immunoblotting with Cdk2 antibody. The arrowheads indicate Cdk2β (upper) and Cdk2α (lower). Scale bars, 10 μm; inset, 2 μm. The uncropped immunoblot is shown in Supplementary Fig. 7.