Figure 4.
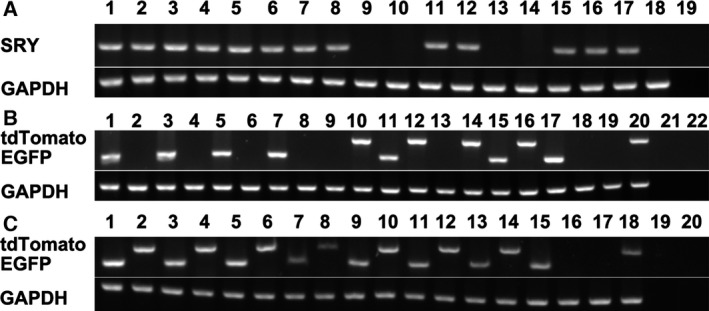
Genotype identification of chimeric piglets by PCR analysis. GAPDH was included as a loading control. (A) SRY gene amplification. Lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15: amplification of genomic DNA from the ears of piglets 2453, 2455, 2457, 2459, 2460, 2461, 2462, and 2463, respectively; lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16: amplification of tail genomic DNA from piglets 2453, 2455, 2457, 2459, 2460, 2461, 2462, and 2463, respectively; lanes 17, 18 and 19: amplification of genomic DNA from EGFP‐expressing cells, tdTomato‐transfected cells and ddH2O (negative control), respectively. (B) The EGFP gene and tdTomato gene were amplified from the genomic DNA of newborn piglets. Lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, and 21: the EGFP gene was detected in the ear genomic DNA from piglets 2453, 2455, 2457, 2459, 2460, 2461, 2462, and 2463; EGFP expressing cells; tdTomato‐transfected cells; and ddH2O (negative control), respectively; lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, and 22: the tdTomato gene was detected in the ear genomic DNA from piglets 2453, 2455, 2457, 2459, 2460, 2461, 2462, and 2463; EGFP‐expressing cells; tdTomato‐transfected cells; and ddH2O (negative control), respectively. (C) The EGFP gene and the tdTomato gene were amplified from genomic DNA from different tissues of Rature. Lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, and 19: the EGFP gene was detected in the genomic DNA from liver, lung, heart, kidney, spleen, skin, testis, EGFP‐expressing cells, tdTomato‐transfected cells and ddH2O (negative control), respectively; lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, and 20: the tdTomato gene was detected in the genomic DNA from liver, lung, heart, kidney, spleen, skin, testis, EGFP‐expressing cells, tdTomato‐transfected cells, and ddH2O (negative control), respectively.
