Figure 2. bCCL19 can detect CCR7 on T cells using flow cytometry.
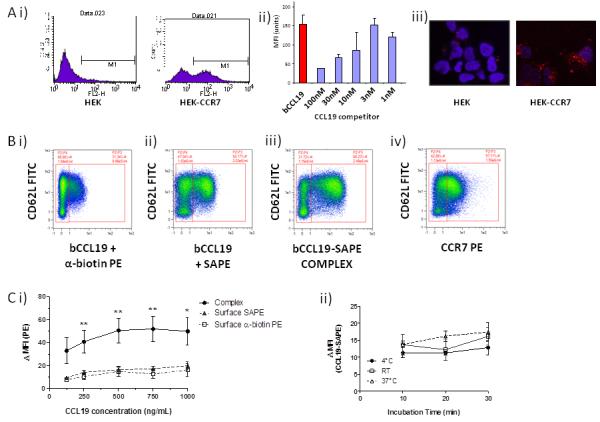
(A) i) Representative flow cytometric data showing the binding of the SAPE tagged bCCL19 to HEK cells transfected with CCR7 (HEK-CCR7) but not to untransfected HEK cells (HEK). ii) The binding of bCCL19 to HEK-CCR7 cells is competable with unlabelled CCL19 (concentrations in nM). iii) confocal imaging demonstrating the uptake of PE-tagged bCCL19 into intracellular vesicles in HEK-CCR7, but not HEK, cells. All of the above experiments in were performed at 37°C. (B) Representative dot-plots of T cells stained with (i) bCCL19 followed by antibiotin-PE antibody; (ii) bCCL19 followed by SAPE; (iii) pre-complexed bCCL19-SAPE; (iv) CCR7-PE antibody. Plots taken from one donor with 250ng/mL bCCL19 used for staining, with gating to indicate positive and negative populations. (C) Optimisation of staining protocol using human T cells. (i) T cells were stained using either pre-complexed bCCL19-SAPE (circles), or with bCCL19 alone, followed by surface staining with either SAPE (triangles) or anti-biotin PE (squares) (n = 4 different donors. Data represents mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA [125] p = 0.1; [250] **p = 0.0056; [500] **p = 0.0076; [750] **p = 0.0059; [1000] *p = 0.025). Data are expressed as ΔMFI, which was calculated as [MFI of CCR7/CD62L-positive population]/[MFI of CCR7/CD62L-negative population]. (ii) T cells were incubated with 250 ng/mL CCL19-SAPE complex at 3 different temperatures for increasing lengths of time to determine effects on staining as described above (n = 2 different donors).
