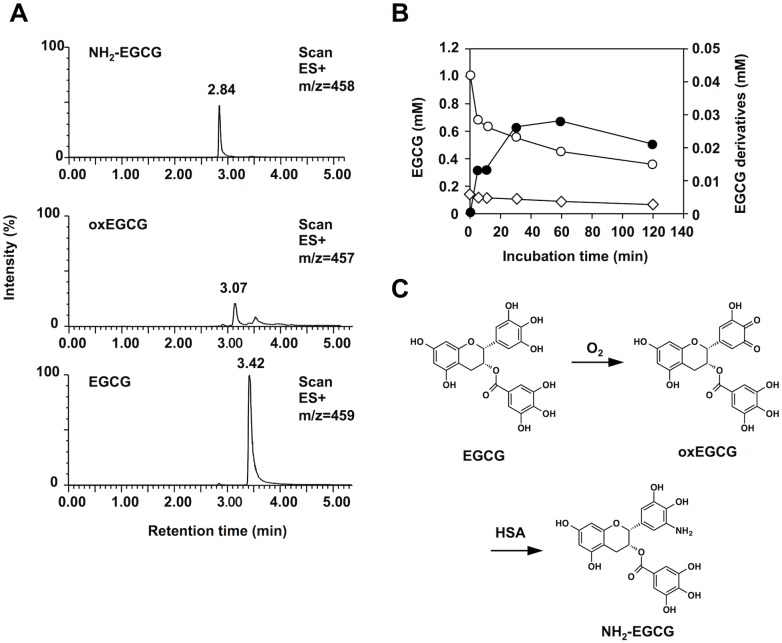
Fig 2. LC-ESI-MS analysis of oxidized and aminated EGCGs.
(A) Selected ion-current chromatograms monitored with m/z 459 (M+H)+, m/z 457 (M+H)+, and m/z 458 (M+H)+ for EGCG, oxEGCG, and NH2-EGCG, respectively. HSA (1 mg/ml) was incubated with 1 mM EGCG in PBS (pH 7.4) at 37°C and the products were analyzed by LC-ESI-MS in the positive ion mode. (B) Time-dependent consumption of EGCG and concomitant formation of oxEGCG and NH2-EGCG. The EGCG-derived products were quantitated as EGCG equivalents. Symbols: open circle, EGCG; open triangle, oxEGCG; closed circle, NH2-EGCG. (C) A proposed mechanism for the oxidative deamination of lysine residues in proteins by EGCG.