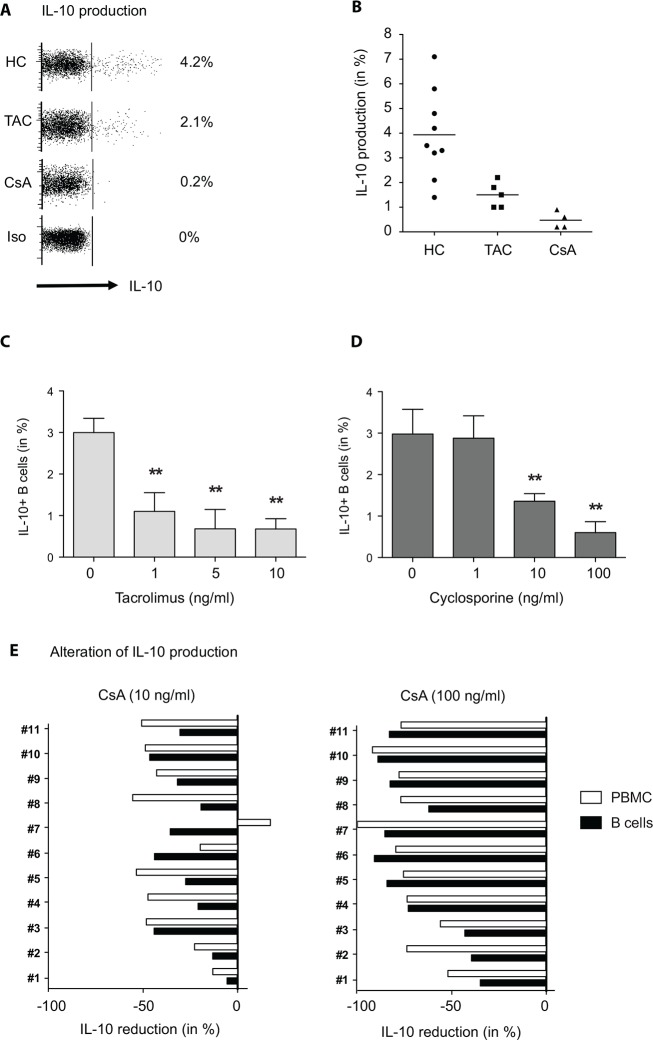
Fig 2. The calcineurin inhibitors tacrolimus and CsA inhibit IL-10 expression of B-cells in vitro and in vivo.
Freshly isolated PBMCs from healthy subjects (n = 9) and renal transplant recipients (n = 9) were mitogen/toll-like-receptor 9 stimulated for 72 hours and subsequently stained for surface CD19 and intracellular IL-10 or with the respective isotype control antibodies (A). The representative dot plots on the upper left in A show the intracellular IL-10 expression of stimulated CD19+ B-cells from a healthy subject and representative renal transplant recipients receiving either tacrolimus or CsA (after gating on CD19+ B-cells). The scatter plot in B summarizes the results of multiple unrelated experiments. PBMCs of healthy subjects were stimulated like described before in presence or absence of different concentrations of tacrolimus (n = 4) (C) or CsA (n = 4) (D), as indicated. The bar graphs in E depict the decline of IL-10 production (in %) of PBMCs vs. positively isolated CD19+ B-cells after stimulation co-cultured with CsA (n = 9 healthy subjects). 7-AAD staining was performed to ensure viability of cell culture.