Figure 4.
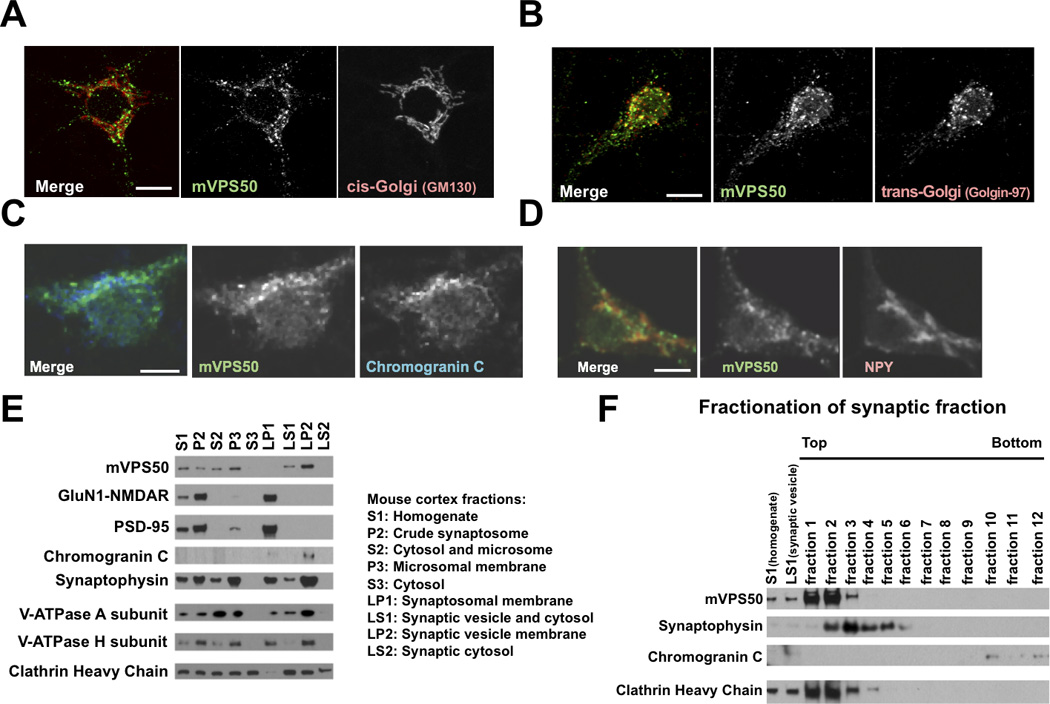
mVPS50 associates with synaptic and dense-core vesicles. A) mVPS50 does not colocalize with the cis-Golgi apparatus (GM130) in mouse primary cultured cortical neurons. B) mVPS50 partially colocalizes with the trans-Golgi apparatus (Golgin-97) in mouse primary cultured cortical neurons. C) mVPS50 partially colocalizes with Chromogranin C-containing dense-core vesicles (ChrC) in mouse primary cultured cortical neurons. D) mVPS50 partially colocalizes with neuropeptide Y-containing dense-core vesicles (NPY) in mouse primary cultured cortical neurons. Endogenous mVPS50, GM130, Golgin-97, ChrC and NPY were detected by immunofluorescence. Scale bar for A–B: 10 µm. Scale bar for C-D: 5 µm. E) mVPS50 significantly cofractionates with the synaptic vesicle protein synaptophysin and the neuropeptide Chromogranin C. Extracts from adult mouse cortex were fractionated, and fractions were probed by immunoblotting for mVPS50, the NMDA glutamate receptor subunit GluN1, the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95, the neuropeptide Chromogranin C, the synaptic vesicle membrane protein synaptophysin, the cytoplasmic V-ATPase A and H subunit (the mammalian homolog of C. elegans VHA-15) and the vesicle coat protein clathrin heavy chain. F) mVPS50 is a soluble protein. The synaptic vesicle and cytosol (LS1) fraction from adult mouse cortex was further fractionated using sucrose gradient centrifugation, and fractions were probed by immunoblotting. See also Figure S3.
